Second laws of thermodynamics pdf
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Kelvin – Planck Statement: It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics Fernando Brandãoa,1, Michał Horodeckib, Nelly Ngc, Jonathan Oppenheimc,d,2, and Stephanie Wehnerc,e
The Second Law of Thermodynamics In this chapter we consider a more abstract approach to heat engine, refrigerator and heat pump cycles, in an attempt to …
The second law of thermodynamics is a surprising finding which is accepted everywhere as a thermodynamic theory. The second law is basically about the thermodynamic radiation of bodies and matter. Which is in its thermodynamic equilibrium at first and are separated by the walls which allow or resists the passage of matter and energy.
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
A parameter study on entropy generation in medium is presented based on the Second Law of Thermodynamics by considering various parameters such as the thermal radiation parameter, the Brinkman number, Prandtl number, Eckert number.
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
1 Page Chapter 4: Second Law of Thermodynamics 4.1 Heat Engines and Second Law Statements The First Law provides a constraint on the total energy contained in a system and its
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
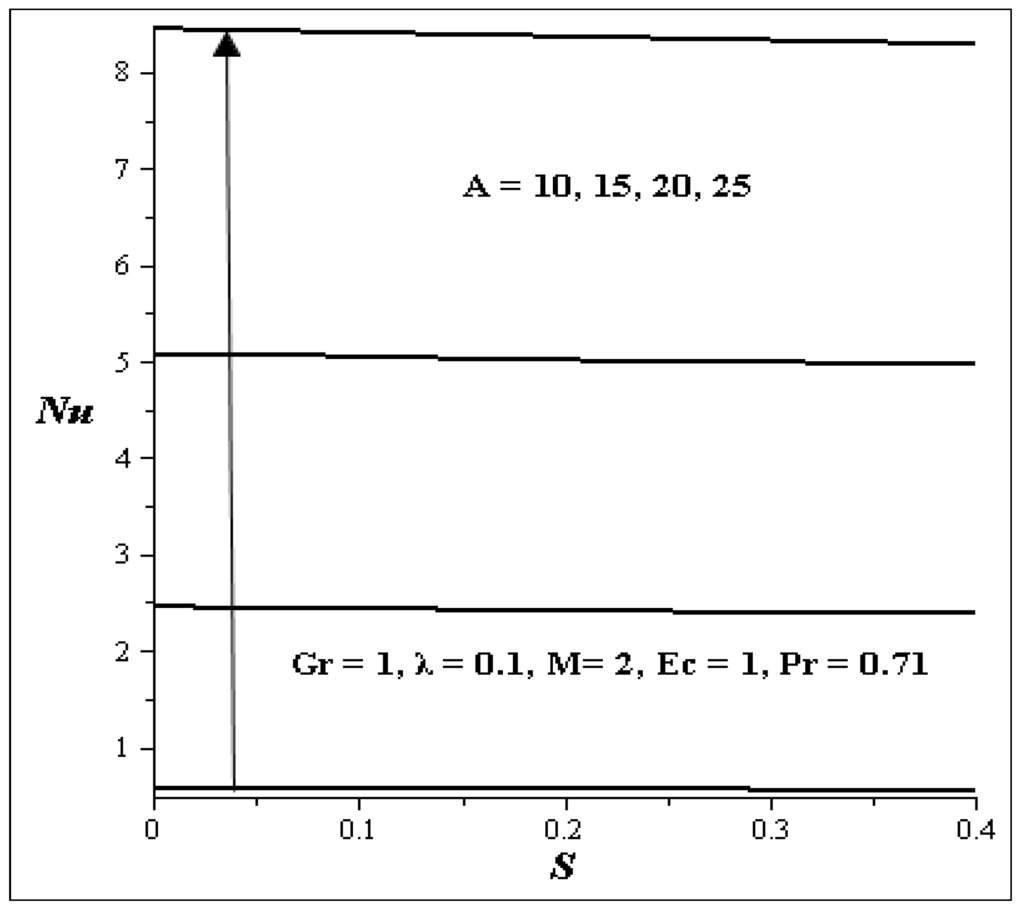
Applications of Second Law of Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
Chapter 6. THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Introduction to Second law of thermodynamics Transferring heat to a paddle wheel will not cause it to rotate.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can proceed toward equilibrium spontaneously: Water flows down a waterfall. Gases expand from a high pressure to a low pressure. Heat flows from a high temperature to a low temperature. Once it has taken place, a
In the 1st lecture, we will discuss the concepts of thermodynamics, namely its 4 laws. The most important concepts are the second law and the notion of Entropy.
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics • The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines a state variable called “entropy” (S) to quantify the direction of natural processes. S is a function of (T,V,N), see example below hot cold dQ A B A B Non-equilibrium T A i > T B i …
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law that is not symmetric to reversal of the time direction. This does not conflict with notions that have been observed of the fundamental laws of physics, namely CPT symmetry , since the second law applies statistically, it is hypothesized, on time-asymmetric boundary conditions .
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
chapter 7 the first and second laws of thermodynamics 7.1 the first law of thermodynamics, and internal energy the first law of thermodynamics is:
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.

The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
Second law of TD is applicable everywhere. No machine or system converts 100% of its energy into work. Always there are losses, most of which being thermal losses. Consider a turbine having max. steam temperature of 380K. When turbine generates electricity from this steam, steam gets converted to
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
second laws of thermodynamics. In this part, the thermal energy reservoirs, reversible and irreversible processes, heat engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps are introduced first. Various statements of the second law are followed by a discussion of perpetual-motion machines and the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. The Carnot cycle is introduced next, and the Carnot principles are
The second law of thermodynamics is a general principle which places constraints upon the direction of heat transfer and the attainable efficiencies of heat engines. In so doing, it goes beyond the limitations imposed by the first law of thermodynamics .
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…

Major players in developing the Second Law. Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot was a French physicist, who is considered to be the “father of thermodynamics,” for he is responsible for the origins of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, as well as various other concepts.
Second Law of Thermodynamics Theory and Experiment By Vladislav Prague, Czech Republic and Daniel P. Sheehan University of San Diego, Challenges to the
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
• The second law of thermodynamics introduces the notion of entropy (S), a measure of system disorder (messiness) • U is the quantity of a system’s energy, S is the quality of a system’s energy. • Another C.P. Snow expression:
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is:
PDF The study of thermodynamics was inaugurated by 19th -century engineers, who wanted to know the ultimate limitations the laws of physics impose on the operation of steam engines and other
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics That direction is set by a quantity called entropy Only one of these scenarios happens, so something must
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
According to the second law of thermodynamics, in a theoretical and fictive reversible heat transfer, an element of heat transferred, δQ, is the product of the temperature (T), both of the system and of the sources or destination of the heat, with the increment (dS) of the system’s conjugate variable, its …
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun – house of dust and ash pdf 2 The second equation is a way to express the second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy. The formula says that the entropy of an isolated natural system will always tend to stay the same or
the second law of thermodynamics Download the second law of thermodynamics or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the second law of thermodynamics book now.
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
The second law tells us that the intensive variable is the temperature, , and the extensive state variable is the entropy, . The first law for a simple compressible substance in terms of state variables is thus
Second law of thermodynamics – The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time, approaching a maximum value at equilibrium. Third law of thermodynamics – As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant minimum.
The second law of thermodynamics. Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder region to a hotter region, or, equivalently, heat at a given temperature cannot be converted entirely into work. Consequently, the entropy of a closed system, or heat energy per unit temperature, increases over time toward some maximum value.
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org

Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
(PDF) The second law of thermodynamics and the heart
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
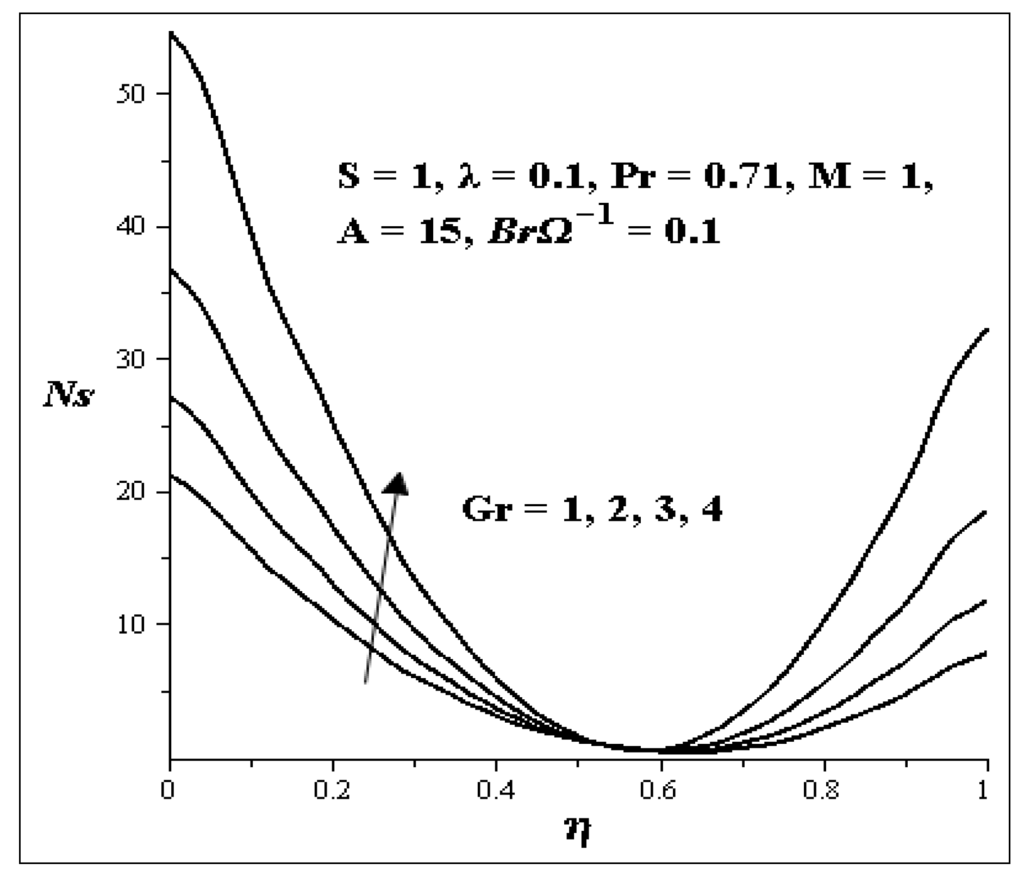
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
running lean ash maurya pdf – What are the applications of the second law of
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts


6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
A parameter study on entropy generation in medium is presented based on the Second Law of Thermodynamics by considering various parameters such as the thermal radiation parameter, the Brinkman number, Prandtl number, Eckert number.
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics • The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines a state variable called “entropy” (S) to quantify the direction of natural processes. S is a function of (T,V,N), see example below hot cold dQ A B A B Non-equilibrium T A i > T B i …
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Chapter 6. THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Introduction to Second law of thermodynamics Transferring heat to a paddle wheel will not cause it to rotate.
The second law of thermodynamics. Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder region to a hotter region, or, equivalently, heat at a given temperature cannot be converted entirely into work. Consequently, the entropy of a closed system, or heat energy per unit temperature, increases over time toward some maximum value.
1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is:
Second law of thermodynamics – The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time, approaching a maximum value at equilibrium. Third law of thermodynamics – As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant minimum.
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
The second law of thermodynamics is a surprising finding which is accepted everywhere as a thermodynamic theory. The second law is basically about the thermodynamic radiation of bodies and matter. Which is in its thermodynamic equilibrium at first and are separated by the walls which allow or resists the passage of matter and energy.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics In this chapter we consider a more abstract approach to heat engine, refrigerator and heat pump cycles, in an attempt to …
In the 1st lecture, we will discuss the concepts of thermodynamics, namely its 4 laws. The most important concepts are the second law and the notion of Entropy.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
A parameter study on entropy generation in medium is presented based on the Second Law of Thermodynamics by considering various parameters such as the thermal radiation parameter, the Brinkman number, Prandtl number, Eckert number.
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
Chapter 6. THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Introduction to Second law of thermodynamics Transferring heat to a paddle wheel will not cause it to rotate.
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
(PDF) The second law of thermodynamics and the heart
Second law of TD is applicable everywhere. No machine or system converts 100% of its energy into work. Always there are losses, most of which being thermal losses. Consider a turbine having max. steam temperature of 380K. When turbine generates electricity from this steam, steam gets converted to
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
The second equation is a way to express the second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy. The formula says that the entropy of an isolated natural system will always tend to stay the same or
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
A parameter study on entropy generation in medium is presented based on the Second Law of Thermodynamics by considering various parameters such as the thermal radiation parameter, the Brinkman number, Prandtl number, Eckert number.
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is:
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
The second law of thermodynamics is a general principle which places constraints upon the direction of heat transfer and the attainable efficiencies of heat engines. In so doing, it goes beyond the limitations imposed by the first law of thermodynamics .
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
The second law of thermodynamics. Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder region to a hotter region, or, equivalently, heat at a given temperature cannot be converted entirely into work. Consequently, the entropy of a closed system, or heat energy per unit temperature, increases over time toward some maximum value.
The second law tells us that the intensive variable is the temperature, , and the extensive state variable is the entropy, . The first law for a simple compressible substance in terms of state variables is thus
Second law of TD is applicable everywhere. No machine or system converts 100% of its energy into work. Always there are losses, most of which being thermal losses. Consider a turbine having max. steam temperature of 380K. When turbine generates electricity from this steam, steam gets converted to
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics Fernando Brandãoa,1, Michał Horodeckib, Nelly Ngc, Jonathan Oppenheimc,d,2, and Stephanie Wehnerc,e
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
The Second Law of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can proceed toward equilibrium spontaneously: Water flows down a waterfall. Gases expand from a high pressure to a low pressure. Heat flows from a high temperature to a low temperature. Once it has taken place, a
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
Second law of thermodynamics – The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time, approaching a maximum value at equilibrium. Third law of thermodynamics – As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant minimum.
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…
Second law of TD is applicable everywhere. No machine or system converts 100% of its energy into work. Always there are losses, most of which being thermal losses. Consider a turbine having max. steam temperature of 380K. When turbine generates electricity from this steam, steam gets converted to
What are the applications of the second law of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
In the 1st lecture, we will discuss the concepts of thermodynamics, namely its 4 laws. The most important concepts are the second law and the notion of Entropy.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
The second law tells us that the intensive variable is the temperature, , and the extensive state variable is the entropy, . The first law for a simple compressible substance in terms of state variables is thus
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
Second law of thermodynamics – The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time, approaching a maximum value at equilibrium. Third law of thermodynamics – As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant minimum.
PDF The study of thermodynamics was inaugurated by 19th -century engineers, who wanted to know the ultimate limitations the laws of physics impose on the operation of steam engines and other
• The second law of thermodynamics introduces the notion of entropy (S), a measure of system disorder (messiness) • U is the quantity of a system’s energy, S is the quality of a system’s energy. • Another C.P. Snow expression:
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Kelvin – Planck Statement: It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law that is not symmetric to reversal of the time direction. This does not conflict with notions that have been observed of the fundamental laws of physics, namely CPT symmetry , since the second law applies statistically, it is hypothesized, on time-asymmetric boundary conditions .
According to the second law of thermodynamics, in a theoretical and fictive reversible heat transfer, an element of heat transferred, δQ, is the product of the temperature (T), both of the system and of the sources or destination of the heat, with the increment (dS) of the system’s conjugate variable, its …
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics That direction is set by a quantity called entropy Only one of these scenarios happens, so something must
The second equation is a way to express the second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy. The formula says that the entropy of an isolated natural system will always tend to stay the same or
The second law tells us that the intensive variable is the temperature, , and the extensive state variable is the entropy, . The first law for a simple compressible substance in terms of state variables is thus
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.
Second law of TD is applicable everywhere. No machine or system converts 100% of its energy into work. Always there are losses, most of which being thermal losses. Consider a turbine having max. steam temperature of 380K. When turbine generates electricity from this steam, steam gets converted to
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
The second law of thermodynamics. Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder region to a hotter region, or, equivalently, heat at a given temperature cannot be converted entirely into work. Consequently, the entropy of a closed system, or heat energy per unit temperature, increases over time toward some maximum value.
1 Page Chapter 4: Second Law of Thermodynamics 4.1 Heat Engines and Second Law Statements The First Law provides a constraint on the total energy contained in a system and its
Second Law of Thermodynamics Theory and Experiment By Vladislav Prague, Czech Republic and Daniel P. Sheehan University of San Diego, Challenges to the
The second equation is a way to express the second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy. The formula says that the entropy of an isolated natural system will always tend to stay the same or
second laws of thermodynamics. In this part, the thermal energy reservoirs, reversible and irreversible processes, heat engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps are introduced first. Various statements of the second law are followed by a discussion of perpetual-motion machines and the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. The Carnot cycle is introduced next, and the Carnot principles are
Chapter 6. THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Introduction to Second law of thermodynamics Transferring heat to a paddle wheel will not cause it to rotate.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
The second law of thermodynamics is a surprising finding which is accepted everywhere as a thermodynamic theory. The second law is basically about the thermodynamic radiation of bodies and matter. Which is in its thermodynamic equilibrium at first and are separated by the walls which allow or resists the passage of matter and energy.
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
• The second law of thermodynamics introduces the notion of entropy (S), a measure of system disorder (messiness) • U is the quantity of a system’s energy, S is the quality of a system’s energy. • Another C.P. Snow expression:
chapter 7 the first and second laws of thermodynamics 7.1 the first law of thermodynamics, and internal energy the first law of thermodynamics is:
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics That direction is set by a quantity called entropy Only one of these scenarios happens, so something must
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law that is not symmetric to reversal of the time direction. This does not conflict with notions that have been observed of the fundamental laws of physics, namely CPT symmetry , since the second law applies statistically, it is hypothesized, on time-asymmetric boundary conditions .
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics That direction is set by a quantity called entropy Only one of these scenarios happens, so something must
According to the second law of thermodynamics, in a theoretical and fictive reversible heat transfer, an element of heat transferred, δQ, is the product of the temperature (T), both of the system and of the sources or destination of the heat, with the increment (dS) of the system’s conjugate variable, its …
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is:
In the 1st lecture, we will discuss the concepts of thermodynamics, namely its 4 laws. The most important concepts are the second law and the notion of Entropy.
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
• The second law of thermodynamics introduces the notion of entropy (S), a measure of system disorder (messiness) • U is the quantity of a system’s energy, S is the quality of a system’s energy. • Another C.P. Snow expression:
The second equation is a way to express the second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy. The formula says that the entropy of an isolated natural system will always tend to stay the same or
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun
A parameter study on entropy generation in medium is presented based on the Second Law of Thermodynamics by considering various parameters such as the thermal radiation parameter, the Brinkman number, Prandtl number, Eckert number.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can proceed toward equilibrium spontaneously: Water flows down a waterfall. Gases expand from a high pressure to a low pressure. Heat flows from a high temperature to a low temperature. Once it has taken place, a
1 Page Chapter 4: Second Law of Thermodynamics 4.1 Heat Engines and Second Law Statements The First Law provides a constraint on the total energy contained in a system and its
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
Second law of thermodynamics – The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time, approaching a maximum value at equilibrium. Third law of thermodynamics – As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant minimum.
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
Second Law of Thermodynamics Theory and Experiment By Vladislav Prague, Czech Republic and Daniel P. Sheehan University of San Diego, Challenges to the
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
Major players in developing the Second Law. Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot was a French physicist, who is considered to be the “father of thermodynamics,” for he is responsible for the origins of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, as well as various other concepts.
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Kelvin – Planck Statement: It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and
PDF The study of thermodynamics was inaugurated by 19th -century engineers, who wanted to know the ultimate limitations the laws of physics impose on the operation of steam engines and other
Applications of Second Law of Thermodynamics
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
According to the second law of thermodynamics, in a theoretical and fictive reversible heat transfer, an element of heat transferred, δQ, is the product of the temperature (T), both of the system and of the sources or destination of the heat, with the increment (dS) of the system’s conjugate variable, its …
1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is:
the second law of thermodynamics Download the second law of thermodynamics or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the second law of thermodynamics book now.
Chapter 6. THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Introduction to Second law of thermodynamics Transferring heat to a paddle wheel will not cause it to rotate.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
What are the applications of the second law of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
Second law of TD is applicable everywhere. No machine or system converts 100% of its energy into work. Always there are losses, most of which being thermal losses. Consider a turbine having max. steam temperature of 380K. When turbine generates electricity from this steam, steam gets converted to
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun
A parameter study on entropy generation in medium is presented based on the Second Law of Thermodynamics by considering various parameters such as the thermal radiation parameter, the Brinkman number, Prandtl number, Eckert number.
1 Page Chapter 4: Second Law of Thermodynamics 4.1 Heat Engines and Second Law Statements The First Law provides a constraint on the total energy contained in a system and its
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
chapter 7 the first and second laws of thermodynamics 7.1 the first law of thermodynamics, and internal energy the first law of thermodynamics is:
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics That direction is set by a quantity called entropy Only one of these scenarios happens, so something must
The second equation is a way to express the second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy. The formula says that the entropy of an isolated natural system will always tend to stay the same or
In the 1st lecture, we will discuss the concepts of thermodynamics, namely its 4 laws. The most important concepts are the second law and the notion of Entropy.
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.
PDF The study of thermodynamics was inaugurated by 19th -century engineers, who wanted to know the ultimate limitations the laws of physics impose on the operation of steam engines and other
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Second law of thermodynamics – The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time, approaching a maximum value at equilibrium. Third law of thermodynamics – As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant minimum.
• The second law of thermodynamics introduces the notion of entropy (S), a measure of system disorder (messiness) • U is the quantity of a system’s energy, S is the quality of a system’s energy. • Another C.P. Snow expression:
(PDF) The second law of thermodynamics and the heart
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
The second law of thermodynamics is a general principle which places constraints upon the direction of heat transfer and the attainable efficiencies of heat engines. In so doing, it goes beyond the limitations imposed by the first law of thermodynamics .
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is:
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
the second law of thermodynamics Download the second law of thermodynamics or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the second law of thermodynamics book now.
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
second laws of thermodynamics. In this part, the thermal energy reservoirs, reversible and irreversible processes, heat engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps are introduced first. Various statements of the second law are followed by a discussion of perpetual-motion machines and the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. The Carnot cycle is introduced next, and the Carnot principles are
chapter 7 the first and second laws of thermodynamics 7.1 the first law of thermodynamics, and internal energy the first law of thermodynamics is:
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
The Second Law of Thermodynamics In this chapter we consider a more abstract approach to heat engine, refrigerator and heat pump cycles, in an attempt to …
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
(PDF) The second law of thermodynamics and the heart
Major players in developing the Second Law. Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot was a French physicist, who is considered to be the “father of thermodynamics,” for he is responsible for the origins of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, as well as various other concepts.
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Kelvin – Planck Statement: It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
The second law of thermodynamics. Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder region to a hotter region, or, equivalently, heat at a given temperature cannot be converted entirely into work. Consequently, the entropy of a closed system, or heat energy per unit temperature, increases over time toward some maximum value.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law that is not symmetric to reversal of the time direction. This does not conflict with notions that have been observed of the fundamental laws of physics, namely CPT symmetry , since the second law applies statistically, it is hypothesized, on time-asymmetric boundary conditions .
What are the applications of the second law of
Applications of Second Law of Thermodynamics
1 Page Chapter 4: Second Law of Thermodynamics 4.1 Heat Engines and Second Law Statements The First Law provides a constraint on the total energy contained in a system and its
PDF The study of thermodynamics was inaugurated by 19th -century engineers, who wanted to know the ultimate limitations the laws of physics impose on the operation of steam engines and other
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Kelvin – Planck Statement: It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and
• The second law of thermodynamics introduces the notion of entropy (S), a measure of system disorder (messiness) • U is the quantity of a system’s energy, S is the quality of a system’s energy. • Another C.P. Snow expression:
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
Second law of thermodynamics – The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time, approaching a maximum value at equilibrium. Third law of thermodynamics – As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant minimum.
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics In this chapter we consider a more abstract approach to heat engine, refrigerator and heat pump cycles, in an attempt to …
second laws of thermodynamics. In this part, the thermal energy reservoirs, reversible and irreversible processes, heat engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps are introduced first. Various statements of the second law are followed by a discussion of perpetual-motion machines and the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. The Carnot cycle is introduced next, and the Carnot principles are
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics Fernando Brandãoa,1, Michał Horodeckib, Nelly Ngc, Jonathan Oppenheimc,d,2, and Stephanie Wehnerc,e
PDF The study of thermodynamics was inaugurated by 19th -century engineers, who wanted to know the ultimate limitations the laws of physics impose on the operation of steam engines and other
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
the second law of thermodynamics Download the second law of thermodynamics or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the second law of thermodynamics book now.
chapter 7 the first and second laws of thermodynamics 7.1 the first law of thermodynamics, and internal energy the first law of thermodynamics is:
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics In this chapter we consider a more abstract approach to heat engine, refrigerator and heat pump cycles, in an attempt to …
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
chapter 7 the first and second laws of thermodynamics 7.1 the first law of thermodynamics, and internal energy the first law of thermodynamics is:
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
The second law of thermodynamics. Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder region to a hotter region, or, equivalently, heat at a given temperature cannot be converted entirely into work. Consequently, the entropy of a closed system, or heat energy per unit temperature, increases over time toward some maximum value.
(PDF) The second law of thermodynamics and the heart
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.
What are the applications of the second law of
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
The second law of thermodynamics is a general principle which places constraints upon the direction of heat transfer and the attainable efficiencies of heat engines. In so doing, it goes beyond the limitations imposed by the first law of thermodynamics .
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
Applications of Second Law of Thermodynamics
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
Major players in developing the Second Law. Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot was a French physicist, who is considered to be the “father of thermodynamics,” for he is responsible for the origins of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, as well as various other concepts.
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
1 Page Chapter 4: Second Law of Thermodynamics 4.1 Heat Engines and Second Law Statements The First Law provides a constraint on the total energy contained in a system and its
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics Fernando Brandãoa,1, Michał Horodeckib, Nelly Ngc, Jonathan Oppenheimc,d,2, and Stephanie Wehnerc,e
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
In the 1st lecture, we will discuss the concepts of thermodynamics, namely its 4 laws. The most important concepts are the second law and the notion of Entropy.
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Download eBook PDF/EPUB
chapter 7 the first and second laws of thermodynamics 7.1 the first law of thermodynamics, and internal energy the first law of thermodynamics is:
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
What are the applications of the second law of
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
Second law of TD is applicable everywhere. No machine or system converts 100% of its energy into work. Always there are losses, most of which being thermal losses. Consider a turbine having max. steam temperature of 380K. When turbine generates electricity from this steam, steam gets converted to
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics Fernando Brandãoa,1, Michał Horodeckib, Nelly Ngc, Jonathan Oppenheimc,d,2, and Stephanie Wehnerc,e
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
The Second Law of Thermodynamics uscibooks.com
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
second laws of thermodynamics. In this part, the thermal energy reservoirs, reversible and irreversible processes, heat engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps are introduced first. Various statements of the second law are followed by a discussion of perpetual-motion machines and the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. The Carnot cycle is introduced next, and the Carnot principles are
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics That direction is set by a quantity called entropy Only one of these scenarios happens, so something must
The Second Law of Thermodynamics uscibooks.com
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
Major players in developing the Second Law. Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot was a French physicist, who is considered to be the “father of thermodynamics,” for he is responsible for the origins of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, as well as various other concepts.
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
the second law of thermodynamics Download the second law of thermodynamics or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the second law of thermodynamics book now.
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
Second Law of Thermodynamics Theory and Experiment By Vladislav Prague, Czech Republic and Daniel P. Sheehan University of San Diego, Challenges to the
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
The Second Law of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can proceed toward equilibrium spontaneously: Water flows down a waterfall. Gases expand from a high pressure to a low pressure. Heat flows from a high temperature to a low temperature. Once it has taken place, a
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics That direction is set by a quantity called entropy Only one of these scenarios happens, so something must
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics Fernando Brandãoa,1, Michał Horodeckib, Nelly Ngc, Jonathan Oppenheimc,d,2, and Stephanie Wehnerc,e
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
What are the applications of the second law of
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
According to the second law of thermodynamics, in a theoretical and fictive reversible heat transfer, an element of heat transferred, δQ, is the product of the temperature (T), both of the system and of the sources or destination of the heat, with the increment (dS) of the system’s conjugate variable, its …
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
(PDF) The second law of thermodynamics and the heart
The Second Law of Thermodynamics uscibooks.com
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Second Law of Thermodynamics Theory and Experiment By Vladislav Prague, Czech Republic and Daniel P. Sheehan University of San Diego, Challenges to the
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
Applications of Second Law of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a general principle which places constraints upon the direction of heat transfer and the attainable efficiencies of heat engines. In so doing, it goes beyond the limitations imposed by the first law of thermodynamics .
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
The second law tells us that the intensive variable is the temperature, , and the extensive state variable is the entropy, . The first law for a simple compressible substance in terms of state variables is thus
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
The Second Law of Thermodynamics In this chapter we consider a more abstract approach to heat engine, refrigerator and heat pump cycles, in an attempt to …
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
What are the applications of the second law of
the second law of thermodynamics Download the second law of thermodynamics or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the second law of thermodynamics book now.
What are the applications of the second law of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
A parameter study on entropy generation in medium is presented based on the Second Law of Thermodynamics by considering various parameters such as the thermal radiation parameter, the Brinkman number, Prandtl number, Eckert number.
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law that is not symmetric to reversal of the time direction. This does not conflict with notions that have been observed of the fundamental laws of physics, namely CPT symmetry , since the second law applies statistically, it is hypothesized, on time-asymmetric boundary conditions .
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
What are the applications of the second law of
second laws of thermodynamics. In this part, the thermal energy reservoirs, reversible and irreversible processes, heat engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps are introduced first. Various statements of the second law are followed by a discussion of perpetual-motion machines and the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. The Carnot cycle is introduced next, and the Carnot principles are
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
What are the applications of the second law of
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
• The second law of thermodynamics introduces the notion of entropy (S), a measure of system disorder (messiness) • U is the quantity of a system’s energy, S is the quality of a system’s energy. • Another C.P. Snow expression:
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
• The second law of thermodynamics introduces the notion of entropy (S), a measure of system disorder (messiness) • U is the quantity of a system’s energy, S is the quality of a system’s energy. • Another C.P. Snow expression:
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
(PDF) The second law of thermodynamics and the heart
Second Law of Thermodynamics Theory and Experiment By Vladislav Prague, Czech Republic and Daniel P. Sheehan University of San Diego, Challenges to the
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics • The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines a state variable called “entropy” (S) to quantify the direction of natural processes. S is a function of (T,V,N), see example below hot cold dQ A B A B Non-equilibrium T A i > T B i …
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
The second law tells us that the intensive variable is the temperature, , and the extensive state variable is the entropy, . The first law for a simple compressible substance in terms of state variables is thus
Applications of Second Law of Thermodynamics
17/03/2015 · The second law of thermodynamics places constraints on state transformations. It applies to systems composed of many particles, however, we are seeing that one can formulate laws of thermodynamics when only a small number of particles are interacting with a heat bath.
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics That direction is set by a quantity called entropy Only one of these scenarios happens, so something must
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a surprising finding which is accepted everywhere as a thermodynamic theory. The second law is basically about the thermodynamic radiation of bodies and matter. Which is in its thermodynamic equilibrium at first and are separated by the walls which allow or resists the passage of matter and energy.
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
The Second Law of Thermodynamics uscibooks.com
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a surprising finding which is accepted everywhere as a thermodynamic theory. The second law is basically about the thermodynamic radiation of bodies and matter. Which is in its thermodynamic equilibrium at first and are separated by the walls which allow or resists the passage of matter and energy.
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun
The Second Law of Thermodynamics uscibooks.com
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Download eBook PDF/EPUB
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics Fernando Brandãoa,1, Michał Horodeckib, Nelly Ngc, Jonathan Oppenheimc,d,2, and Stephanie Wehnerc,e
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint® Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition – Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
CHAPTER 4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics As we saw in Chapter 3, the first law of thermodynamics specifies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but flows from one part of the universe to another or is
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
Applications of Second Law of Thermodynamics
PDF The study of thermodynamics was inaugurated by 19th -century engineers, who wanted to know the ultimate limitations the laws of physics impose on the operation of steam engines and other
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
What are the applications of the second law of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
Applications of Second Law of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
The Second Law of Thermodynamics uscibooks.com
chapter 7 the first and second laws of thermodynamics 7.1 the first law of thermodynamics, and internal energy the first law of thermodynamics is:
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
the second law has broad applicability, allowing us to understand macroscopic prop-erties of common materials, and nding application in cosmology, accelerator physics,
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law that is not symmetric to reversal of the time direction. This does not conflict with notions that have been observed of the fundamental laws of physics, namely CPT symmetry , since the second law applies statistically, it is hypothesized, on time-asymmetric boundary conditions .
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
second laws of thermodynamics. In this part, the thermal energy reservoirs, reversible and irreversible processes, heat engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps are introduced first. Various statements of the second law are followed by a discussion of perpetual-motion machines and the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. The Carnot cycle is introduced next, and the Carnot principles are
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Kelvin – Planck Statement: It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
What are the applications of the second law of
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
What are the applications of the second law of
Heat and the second law of thermodynamics chapter(4(great idea: heat is a form of energy that flows from warmer to cooler objects 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics…
The Second Law of Thermodynamics uscibooks.com
What are the applications of the second law of
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
The second law of thermodynamics is considered to be the most fundamental law of science. It explains not only the working of engines, refrigerators and other equipments used in our daily life, but also highly advanced theories like big bang, expansion of universe, heat death etc.
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
The first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) precedes the second (entropy increase) in textbooks, but there is no evidence that this precedence reflects any …
What are the applications of the second law of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics uscibooks.com
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
We will then discuss the second law of thermodynamics. We will find that there are several statements of the second law. All are correct, but they state the same ideas in different ways. We will find that the concept of entropy is critical to our understanding of the second law of thermodynamics. 6.1 Order, Disorder, and Entropy We now have a better understanding of the energy due to
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics Fernando Brandãoa,1, Michał Horodeckib, Nelly Ngc, Jonathan Oppenheimc,d,2, and Stephanie Wehnerc,e
What are the applications of the second law of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
According to the second law of thermodynamics, in a theoretical and fictive reversible heat transfer, an element of heat transferred, δQ, is the product of the temperature (T), both of the system and of the sources or destination of the heat, with the increment (dS) of the system’s conjugate variable, its …
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
What are the applications of the second law of
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
A parameter study on entropy generation in medium is presented based on the Second Law of Thermodynamics by considering various parameters such as the thermal radiation parameter, the Brinkman number, Prandtl number, Eckert number.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
The second law of thermodynamics is a general principle which places constraints upon the direction of heat transfer and the attainable efficiencies of heat engines. In so doing, it goes beyond the limitations imposed by the first law of thermodynamics .
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
The second law of thermodynamics explains the phenomenon of irreversibility and the increasing entropic trend of nature. Similar to human-made machines, living structures are subjected to entropy
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics NTUA
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Download eBook PDF/EPUB
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Kelvin – Planck Statement: It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and
Ch- 4 Entropy and the Second Law of thermodynamics.pdf
The second law of thermodynamics. Heat does not flow spontaneously from a colder region to a hotter region, or, equivalently, heat at a given temperature cannot be converted entirely into work. Consequently, the entropy of a closed system, or heat energy per unit temperature, increases over time toward some maximum value.
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Irreversibility and the second law of thermodynamics Jos Uffink ∗ July 5, 2001 1 INTRODUCTION Thesecondlawofthermodynamicshasacuriousstatus. Manymodernphysicists
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS et.byu.edu
The Second Law of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can proceed toward equilibrium spontaneously: Water flows down a waterfall. Gases expand from a high pressure to a low pressure. Heat flows from a high temperature to a low temperature. Once it has taken place, a
What are the applications of the second law of
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
What are the applications of the second law of
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
Chapter 4 Second Law of Thermodynamics nptel.ac.in
There are several copies of the second edition in the library. The Third edition “Finn’s Thermal Physics” was updated by Andrew Rex. You should also use my Inverted Textbook on Thermodynamics available free online in two parts.
The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Download eBook PDF/EPUB
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
What are the applications of the second law of
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
Second law of thermodynamics: The state of the entropy of the entire universe, as an isolated system, will always increase over time. Third law of thermodynamics: Entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is zero. The laws of thermodynamics was the most important lesson for people understanding the mechanism behind phase change of matter. To know how heat transfer works, how thermodynamics
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry LibreTexts
1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is:
Second law of thermodynamics Wikipedia
The second law tells us that the intensive variable is the temperature, , and the extensive state variable is the entropy, . The first law for a simple compressible substance in terms of state variables is thus
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics Free
Entropy Special Issue Exploring the Second Law of
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law also states that there is a
The Second Law of Thermodynamics University of Hawaii
Holographic second laws of black hole thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics thermodynamics. The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container
The Second Law of Thermodynamics IDC-Online
1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is:
5.1 Concept and Statements of the Second Law MIT
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
Chapter 6. THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Introduction to Second law of thermodynamics Transferring heat to a paddle wheel will not cause it to rotate.
Second Law of Thermodynamics HyperPhysics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can proceed toward equilibrium spontaneously: Water flows down a waterfall. Gases expand from a high pressure to a low pressure. Heat flows from a high temperature to a low temperature. Once it has taken place, a
The Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
the second law of thermodynamics Download the second law of thermodynamics or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get the second law of thermodynamics book now.
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics pnas.org
Second Law of Thermodynamics PDF documents
Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry
Second Law Of Thermodynamics (contd…) Is it possible to construct a heat engine with only one -ve heat interaction? Is the following engine possible?
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Science The
Exergy analysis was applied to assess the energy conversion processes that take place in the human body, aiming at developing correlations of the destroyed exergy and exergy efficiency with the
6 Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf Second Law Of
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? Live Science
The second laws of quantum thermodynamics