Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex pdf
Although the primary route of information through the layered structure of the primary visual cortex (V1) is generally known, the quantitative details of V1¡s internal transmission are …
The functional architecture of adult cerebral cortex retains a capacity for experience-dependent change. This is seen following focal binocular lesions, which induce rapid changes in receptive field …
RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE ADULT SENSORY CORTEX OF Norman M. Weinberger Department of Psychobiology and Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, University of California, Irvine, California 92717-3800 KEY WORDS: deafferentation, learning, auditory, somatosensory, visual INTRODUCTION A dominant belief in neuroscience is that sensory systems in the adult …
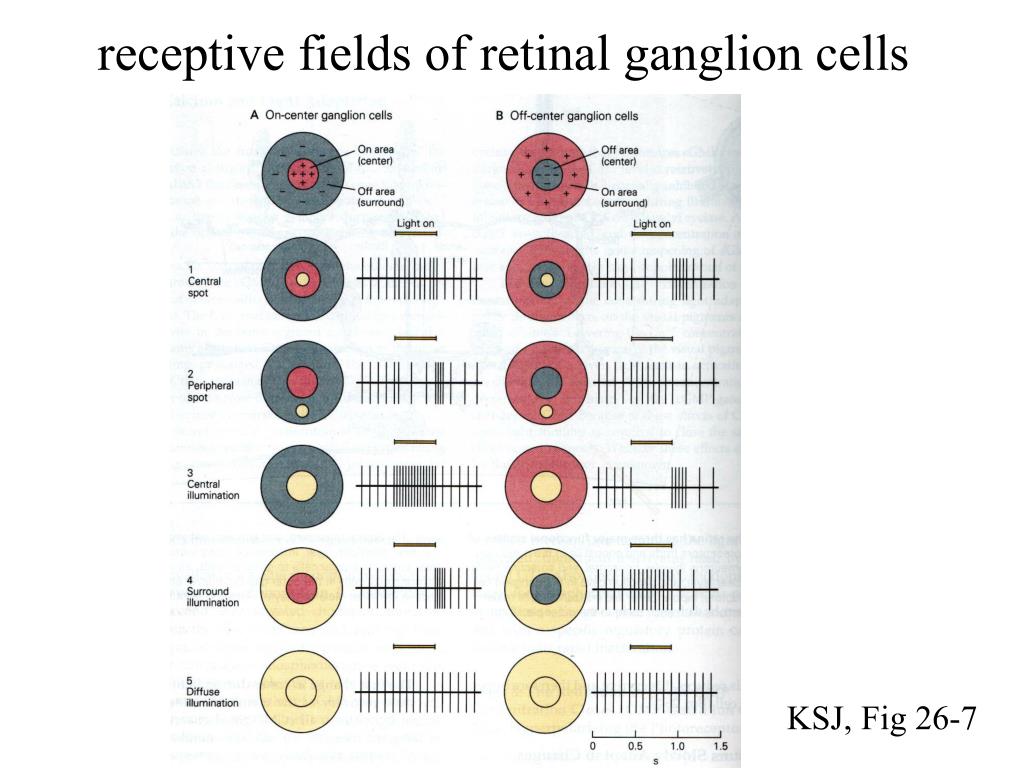
The receptive field of an individual sensory neuron is the particular region of the sensory space (e.g., the body surface, or the visual field) in which a stimulus will modify the firing of that neuron.
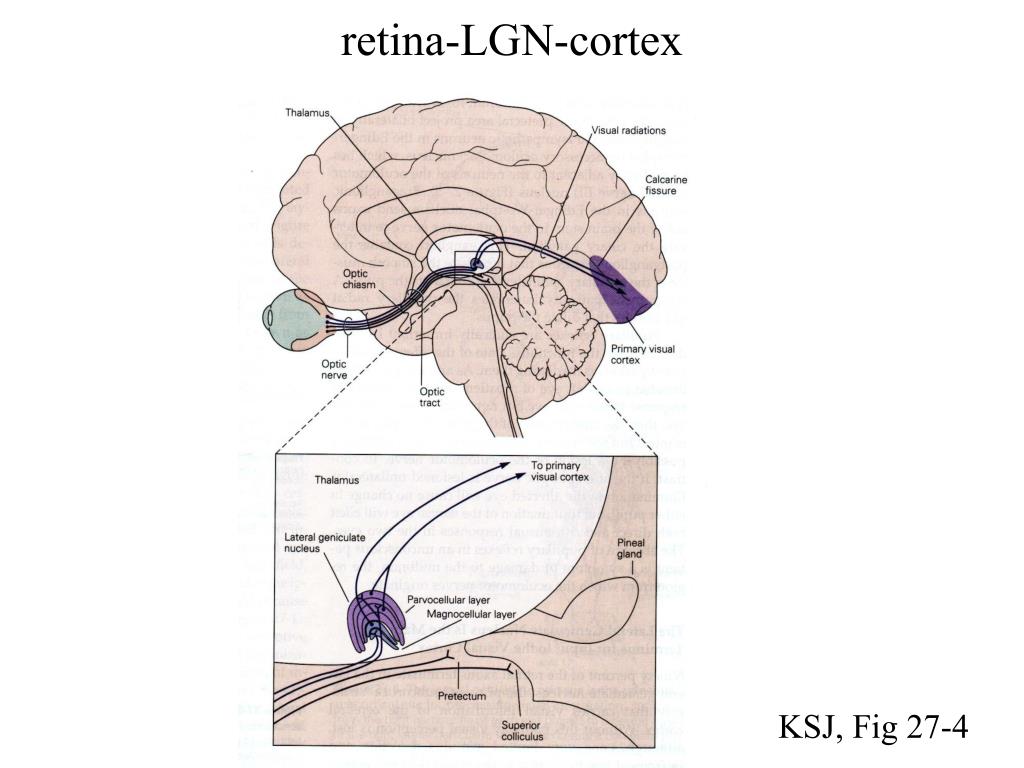
T he Visual Cortex The primary visual cortex lies in the fold of the calcarine sulcus. The fovea is represented at the posterior end of the calcarine sulcus. This small part of the retina has an expanded representation, which occupies about half of the primary visual cortex. The remaining peripheral retina is represented at the anterior half. Things above the line of sight are represented
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex Koen V. Haak1,2, Frans W. Cornelissen1, Antony B. Morland2,3* 1 Laboratory for Experimental Ophthalmology and BCN Neuroimaging Center, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2 York Neuroimaging Centre, Department of Psychology
Seminal work in the early nineties revealed that the visual receptive field of neurons in cat primary visual cortex can change in location and size when artificial scotomas are applied. Recent work now suggests that these single neuron receptive field dynamics also pertain to the neuronal population
In contrast to somatosensory cortex (SI), where the pervasiveness of reorganizational capacities is well-established, plasticity of receptive fields (RFs) of adult primary visual cortex (VI) remains controversial. To investigate RF plasticity in VI of adult rats, we here used intracortical
In binocular regions of primary visual cortex (V1), MD during the developmental critical period causes a decrease in responses to the deprived eye followed by an increase in the nondeprived eye response (Wiesel and Hubel 1963).
Receptive field plasticity of area 17 visual cortical

Receptive field an overview ScienceDirect Topics
A model network of spiking neurons with lateral connections was used to simulate short-term receptive field (RF) changes by removal of afferent input in the primary visual system.
receptive fields recorded from the different layers of the cat’s primary visual cortex. We used whole-cell recording in vivo to show the spatial distribution of visually evoked excitatory and inhibitory inputs and to stain individual neurons.
PDF Seminal work in the early nineties revealed that the visual receptive field of neurons in cat primary visual cortex can change in location and size when artificial scotomas are applied.
The effects of chronic primary visual cortex lesions on receptive fields in the striate cortex have so far not been investigated. The adult visual cortex has, however, a remarkable potential for plasticity, as has been shown by the extensive reorganization following retinal lesions in cat ( Kaas et al. , 1990 ) and monkey ( Heinen and Skavenski, 1991 ; Gilbert and Wiesel, 1992 ).
respond to only a certain part of the visual field. The receptive field size of neurons in primary visual cortex is larger than the ones in the retina and LGN and can typically encompass about 1 degree of visual angle. The connections from the LGN to primary visual cortex are topographically organized, meaning that nearby neurons in the LGN map onto nearby neurons in primary visual cortex

Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat visual cortex Volchan, Eliane; Gilbert, Charles D. 1995-01-01 00:00:00 Receptive fields in primary visual cortex have been shown to be capable of rapid expansion and contraction when exposed to an artificial scotoma, a masked segment of the visual field. To distinguish cortical from thalamic contributions to receptive field mutability
Receptive-field properties of deafferentated visual cortical neurons after topographic map reorganization in adult cats. Journal of Neuroscience 15 , 2417 – 2433 .
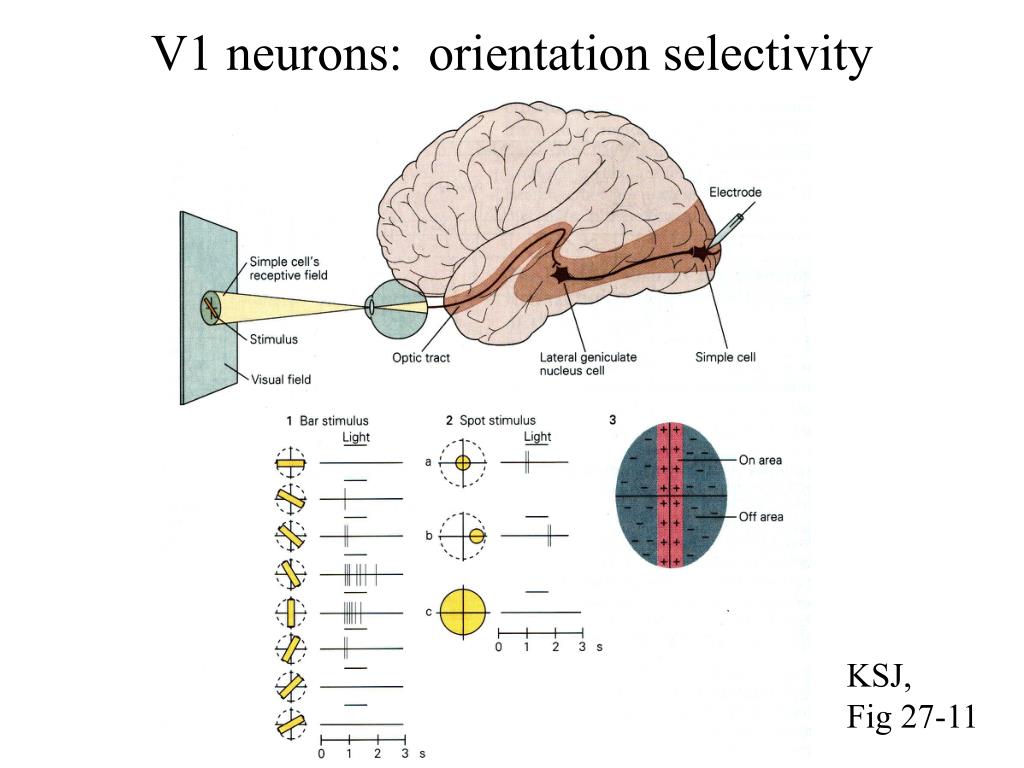
In primary visual cortex, neurons are classified into simple cells and complex cells based on their response properties. Although the role of these two cell types in vision is still unknown, an attractive hypothesis is that simple cells are necessary to construct complex receptive fields.
Furthermore, the assembly of contours and surfaces into unified percepts was assumed to take place at high levels in the visual pathway, whereas the receptive fields of cells in primary visual cortex represented very small windows on the visual scene. These concepts of spatial integration and plasticity have been radically modified in the past few years. The emerging view is that even at the
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex: Receptive Field Analysis of Nearby Neurons Gregory C. DeAngelis, Geoffrey M. Ghose, Izumi Ohzawa, and Ralph D. Freeman Vision Science Group, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720-2020 It is well established that multiple stimulus dimensions (e.g., orientation and spatial frequency) are mapped onto the surface of …
directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat Ausra Daugirdiene 1 *, Algimantas Svegzda 2 , Romualdas Satinskas 2 , Henrikas Vaitkevicius 2
DESCRIPTION. Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex. Charles D. Gilbert & Torsten N. Wiesel Group B6 Margarita Blajeva Caitlin H. Cheong Pari Chowdhary Wissam A. Samad Brooke Thornton.
Abstract THE adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of cortical topography 1-10.
Receptive Fields of Visual Neurons in Primary Auditory Cortex Anna W. Roe,a Sarah L. Pallaqb Young H. Kwon, and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139

These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
1. Receptive field (RF) sizes of neurons in adult primary visual cortex are dynamic, expanding and contracting in response to alternate stimulation outside and within the RF over periods ranging from seconds to minutes.
Shevelev, The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex, Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, 41, 9, …
Ausra Daugirdiene, Algimantas Svegzda, Romualdas Satinskas and Henrikas Vaitkevicius, Detection of the movement direction by the cells with directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat, Health, 02, 10, (1232), (2010).
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
A simple cell in the primary visual cortex is a cell that responds primarily to oriented edges and gratings (bars of particular orientations). These cells were discovered by Torsten Wiesel and David Hubel in the late 1950s.
Since motion in our visual field is continuous, the signals received by the visual system contain an abundance of transient components in the contrast domain. Here using a modified reverse correlation method, we studied the properties of responses of neurons in the cat primary visual cortex to different contrasts of grating stimuli presented statically and transiently for 40 ms, and showed
of neuronal plasticity in adult visual cortex over a wide range of time scales, ranging from minutes to months. As with the other systems, one can also induce plasticity in the visual system with peripheral lesions. Focal retinal lesions, induced with lasers, lead over a period of months to a shrinkage in the cortical representation of the lesioned part of the retina and an increase in the
Population receptive field dynamics in human visual cortex
Visual input to the medial monocular part of rat primary visual cortex was removed by laser coagulation of a small, ≈1-mm-diameter, patch of the upper retina just dorsal to the optic disc.
of signal processing occurs within primary visual cortex. We postulate that the use of natural image sequences may reveal aspects of cortical processing that are not evident when using simpler stimuli such as bars and luminance modulated gratings. Because the cortex is a nonlinear network, it may not be feasi-ble to use the neural responses to simple stimuli to predict and understand cortical
Auditory space-time receptive field dynamics are described with a new investigative tool that is grounded in the theory of white-noise analysis and reverse-correlation techniques.
We studied changes in the spatial parameters of receptive fields (RFs) of visually sensitive neurons in the associative area 21a of the cat cortex under conditions of presentation of moving visual stimuli. The results of experiments demonstrated that these parameters are dynamic and depend, from
The response of a neuron in primary visual cortex (V1) to an optimal stimulus in its classical receptive field (CRF) can be reduced by the presence of an orthogonal mask, a phenomenon known as cross-orientation suppression. The presence of a parallel stimulus outside the CRF can have a similar
In the visual cortex little is known about the effect of dark adaptation on receptive field properties of cells. Two studies in cats have looked at the effects of dark adaptation on orientation selectivity in V-1: both found a persistence of orientation tuning ( Bisti, Clement, Maffei and Mecacci, 1977 ; Ramoa, Freeman and Macy, 1985 ).
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex. Cortical receptive fields are diverse and highly dynamic to accommodate the constantly changing visual environment. The mechanisms behind the organisation of different types of receptive fields are still highly debated
The adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR ORIENTATION DYNAMICS OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS IN THE PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX OF THE CAT Michael A. Repucci, Ferenc Mechler, and Jonathan D. Victor – fly ash concrete mix design pdf aggregate Abstract: A key emergent property of the primary visual cortex (V1) is the orientation selectivity of its neurons. Recent Recent experiments demonstrate remarkable bottom-up and top-down plasticity in orientation networks of the adult cortex.
Nearly 40 years ago, in the pages of this journal, Hubel and Wiesel provided the first description of receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of higher mammals. They defined two classes of cortical cells, ‘simple’ and ‘complex’, based on neural responses to simple visual stimuli. The
CB1 in the primary visual cortex (V1) of the adult primate [18], suggests that cannabinoid mediation of sensory information occurs in the adult as well, and at the earliest stages of cortical processing.
Abstract. Visual receptive fields (RFs) were mapped inside and outside the cortical representation of the optic disk in the striate cortex (area V1) of anesthetized and paralyzed Cebus monkeys.
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex Koen V. Haak1,2, Frans W. Cornelissen1, Antony B. Morland2,3* 1Laboratory for Experimental Ophthalmology and BCN Neuroimaging Center, University Medical Center Groningen, University …
Receptive fields of neurons in the primary visual cortex typically consist of an elongated excitatory field center that determines the orientation specificity of the neuron. The neuron is most strongly activated by light falling on the receptive field center without extending on the inhibitory surround.
The study was performed on neurons with direction selective (DS) receptive fields (RFs) in the primary visual cortex of the cat. Preferred directions (PDs) of these cells to a single light spot and a system of two identical light spots moving across the RF with a given angle between them were compared.
2.3 Primary visual cortex Axons from the optic radiation synapse on layer IV neurons of the primary visual cortex (also known as area 17 cat, striate cortex or V1).
with the spatial receptive fields of simple cells in primary visual cortex. To better quantify the match, To better quantify the match, we compare five properties of model neuron receptive fields to data from macaque V1, namely the
Feedback of this sort can allow rapid, experience-dependent changes in gain control and receptive field dynamics of the more peripheral structure, which in turn can influence subsequent cortical receptive fields [e.g. the visual system (Murphy and Sillito, 1987; Cudeiro et al., 2000)]. The second major similarity between the olfactory cortex and thalamocortical systems is the presence of
1. Cells in area 17 of the cat visual cortex were studied with a view towards correlating receptive field properties with layering. A number of receptive field parameters were measured for all units, and nearly every unit was marked with a microlesion to determine accurately the layer in which it was found.
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex
Gilbert CD, Wiesel TN (1992) Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex. Nature 356:150–152 PubMed CrossRef Google Scholar Hawken MJ, Parker AJ (1987) Spatial properties of neurons in the monkey striate cortex.
Mimicking a retinal lesion with an ‘artificial scotoma’, a large field of moving lines or blinking dots surrounding an occluded area that is positioned to include a cell’s receptive field, causes the receptive field to expand to fill the scotoma .
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex.
The visual cortex of the brain is a part of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Visual nerves run straight from the eye to the primary visual cortex to the Visual Association cortex.
geniculate nucleus (LGN) and in primary visual cortex (V1). In the following, I refer to a In the following, I refer to a “suppressive field” as though this term had wide acceptance.
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author.
Dynamics of neuronal processing in rat somatosensory cortex Christopher I. Moore, Sacha B. Nelson and Mriganka Sur Recently,the study of sensory cortex has focused on the context-dependent evolution of receptive fields and cortical maps over millisecond to second timescales.This article reviews advances in our understanding of these processes in the rat primary somatosensory cortex (SI
Abstract. Neurons in primary visual cortex (area 17) respond vigorously to oriented stimuli within their receptive fields; however, stimuli presented outside the suprathreshold receptive field can also influence their responses.
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Color Neurons in Primary Visual Cortex under Adapting and Non-adapting Conditions Bevil R. Conway, Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115. bconway@hms.harvard.edu
Dynamics of Suppression in Macaque Primary Visual Cortex
Receptive field structure of neurons in monkey primary
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex Brian J. Malone,1 Vikas R. Kumar,3 and Dario L. Ringach2 1Department of Neurobiology, David Geffen School of Medicine, and 2Department of Psychology, University of California,
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex The mammalian primary visual cortex (V1) plays an inte-gral role in many discrimination, recognition and classi-fication tasks. It performs diverse functions, and is well known to be immensely complex. As a dynamical system, V1 likely demands many degrees of freedom to support the great variety of dynamical processes accompanying its …
The position, size, and shape of the receptive field (RF) of some cortical neurons change dynamically, in response to artificial scotoma conditioning (Pettet & Gilbert, 1992) and to retinal
1/08/2004 · In macaque primary visual cortex, I used a modification of the reverse correlation method where the receptive field is probed with a fast sequence of gratings and found that the receptive field shapes were similar to those seen in cat (Ringach, 2002).
C.I. Moore REVIEW Dynamics of neuronal processing in rat

Receptive field organization of complex cells in the cat’s
The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology , Vol. 41, Issue. 9, p. 951.
10/10/1995 · These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex

Primary visual cortex anatomy physiology and functions
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary
parkside ash vacuum cleaner instructions – Chapter 5 Primary visual cortex klab.tch.harvard.edu
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Neurons in Primary

Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex
Adult Cortical Dynamics Physiological Reviews
Strengthening of lateral activation in adult rat visual
Receptive field plasticity of area 17 visual cortical
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
In primary visual cortex, neurons are classified into simple cells and complex cells based on their response properties. Although the role of these two cell types in vision is still unknown, an attractive hypothesis is that simple cells are necessary to construct complex receptive fields.
respond to only a certain part of the visual field. The receptive field size of neurons in primary visual cortex is larger than the ones in the retina and LGN and can typically encompass about 1 degree of visual angle. The connections from the LGN to primary visual cortex are topographically organized, meaning that nearby neurons in the LGN map onto nearby neurons in primary visual cortex
Mimicking a retinal lesion with an ‘artificial scotoma’, a large field of moving lines or blinking dots surrounding an occluded area that is positioned to include a cell’s receptive field, causes the receptive field to expand to fill the scotoma .
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex.
Receptive field Wikipedia
Receptive field organization of complex cells in the cat’s
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex The mammalian primary visual cortex (V1) plays an inte-gral role in many discrimination, recognition and classi-fication tasks. It performs diverse functions, and is well known to be immensely complex. As a dynamical system, V1 likely demands many degrees of freedom to support the great variety of dynamical processes accompanying its …
Since motion in our visual field is continuous, the signals received by the visual system contain an abundance of transient components in the contrast domain. Here using a modified reverse correlation method, we studied the properties of responses of neurons in the cat primary visual cortex to different contrasts of grating stimuli presented statically and transiently for 40 ms, and showed
Abstract: A key emergent property of the primary visual cortex (V1) is the orientation selectivity of its neurons. Recent Recent experiments demonstrate remarkable bottom-up and top-down plasticity in orientation networks of the adult cortex.
These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
Furthermore, the assembly of contours and surfaces into unified percepts was assumed to take place at high levels in the visual pathway, whereas the receptive fields of cells in primary visual cortex represented very small windows on the visual scene. These concepts of spatial integration and plasticity have been radically modified in the past few years. The emerging view is that even at the
In primary visual cortex, neurons are classified into simple cells and complex cells based on their response properties. Although the role of these two cell types in vision is still unknown, an attractive hypothesis is that simple cells are necessary to construct complex receptive fields.
The response of a neuron in primary visual cortex (V1) to an optimal stimulus in its classical receptive field (CRF) can be reduced by the presence of an orthogonal mask, a phenomenon known as cross-orientation suppression. The presence of a parallel stimulus outside the CRF can have a similar
Receptive fields of neurons in the primary visual cortex typically consist of an elongated excitatory field center that determines the orientation specificity of the neuron. The neuron is most strongly activated by light falling on the receptive field center without extending on the inhibitory surround.
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
We studied changes in the spatial parameters of receptive fields (RFs) of visually sensitive neurons in the associative area 21a of the cat cortex under conditions of presentation of moving visual stimuli. The results of experiments demonstrated that these parameters are dynamic and depend, from
receptive fields recorded from the different layers of the cat’s primary visual cortex. We used whole-cell recording in vivo to show the spatial distribution of visually evoked excitatory and inhibitory inputs and to stain individual neurons.
Visual input to the medial monocular part of rat primary visual cortex was removed by laser coagulation of a small, ≈1-mm-diameter, patch of the upper retina just dorsal to the optic disc.
Learning Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning
Rapid Dynamics of Contrast Responses in the Cat Primary
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat visual cortex Volchan, Eliane; Gilbert, Charles D. 1995-01-01 00:00:00 Receptive fields in primary visual cortex have been shown to be capable of rapid expansion and contraction when exposed to an artificial scotoma, a masked segment of the visual field. To distinguish cortical from thalamic contributions to receptive field mutability
of signal processing occurs within primary visual cortex. We postulate that the use of natural image sequences may reveal aspects of cortical processing that are not evident when using simpler stimuli such as bars and luminance modulated gratings. Because the cortex is a nonlinear network, it may not be feasi-ble to use the neural responses to simple stimuli to predict and understand cortical
Shevelev, The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex, Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, 41, 9, …
RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE ADULT SENSORY CORTEX OF Norman M. Weinberger Department of Psychobiology and Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, University of California, Irvine, California 92717-3800 KEY WORDS: deafferentation, learning, auditory, somatosensory, visual INTRODUCTION A dominant belief in neuroscience is that sensory systems in the adult …
Dynamics of neuronal processing in rat somatosensory cortex Christopher I. Moore, Sacha B. Nelson and Mriganka Sur Recently,the study of sensory cortex has focused on the context-dependent evolution of receptive fields and cortical maps over millisecond to second timescales.This article reviews advances in our understanding of these processes in the rat primary somatosensory cortex (SI
CB1 in the primary visual cortex (V1) of the adult primate [18], suggests that cannabinoid mediation of sensory information occurs in the adult as well, and at the earliest stages of cortical processing.
Highly Specific Structural Plasticity of Inhibitory
Rapid Dynamics of Contrast Responses in the Cat Primary
geniculate nucleus (LGN) and in primary visual cortex (V1). In the following, I refer to a In the following, I refer to a “suppressive field” as though this term had wide acceptance.
A simple cell in the primary visual cortex is a cell that responds primarily to oriented edges and gratings (bars of particular orientations). These cells were discovered by Torsten Wiesel and David Hubel in the late 1950s.
The effects of chronic primary visual cortex lesions on receptive fields in the striate cortex have so far not been investigated. The adult visual cortex has, however, a remarkable potential for plasticity, as has been shown by the extensive reorganization following retinal lesions in cat ( Kaas et al. , 1990 ) and monkey ( Heinen and Skavenski, 1991 ; Gilbert and Wiesel, 1992 ).
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex: Receptive Field Analysis of Nearby Neurons Gregory C. DeAngelis, Geoffrey M. Ghose, Izumi Ohzawa, and Ralph D. Freeman Vision Science Group, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720-2020 It is well established that multiple stimulus dimensions (e.g., orientation and spatial frequency) are mapped onto the surface of …
10/10/1995 · These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
Although the primary route of information through the layered structure of the primary visual cortex (V1) is generally known, the quantitative details of V1¡s internal transmission are …
The adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of
Receptive field structure of neurons in monkey primary
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in
Receptive-field properties of deafferentated visual cortical neurons after topographic map reorganization in adult cats. Journal of Neuroscience 15 , 2417 – 2433 .
The response of a neuron in primary visual cortex (V1) to an optimal stimulus in its classical receptive field (CRF) can be reduced by the presence of an orthogonal mask, a phenomenon known as cross-orientation suppression. The presence of a parallel stimulus outside the CRF can have a similar
In primary visual cortex, neurons are classified into simple cells and complex cells based on their response properties. Although the role of these two cell types in vision is still unknown, an attractive hypothesis is that simple cells are necessary to construct complex receptive fields.
Auditory space-time receptive field dynamics are described with a new investigative tool that is grounded in the theory of white-noise analysis and reverse-correlation techniques.
The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology , Vol. 41, Issue. 9, p. 951.
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex The mammalian primary visual cortex (V1) plays an inte-gral role in many discrimination, recognition and classi-fication tasks. It performs diverse functions, and is well known to be immensely complex. As a dynamical system, V1 likely demands many degrees of freedom to support the great variety of dynamical processes accompanying its …
These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat visual cortex Volchan, Eliane; Gilbert, Charles D. 1995-01-01 00:00:00 Receptive fields in primary visual cortex have been shown to be capable of rapid expansion and contraction when exposed to an artificial scotoma, a masked segment of the visual field. To distinguish cortical from thalamic contributions to receptive field mutability
The adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of
A simple cell in the primary visual cortex is a cell that responds primarily to oriented edges and gratings (bars of particular orientations). These cells were discovered by Torsten Wiesel and David Hubel in the late 1950s.
Bottom-up and top-down dynamics in visual cortex
(PDF) Models of Receptive Field Dynamics in Visual Cortex
The effects of chronic primary visual cortex lesions on receptive fields in the striate cortex have so far not been investigated. The adult visual cortex has, however, a remarkable potential for plasticity, as has been shown by the extensive reorganization following retinal lesions in cat ( Kaas et al. , 1990 ) and monkey ( Heinen and Skavenski, 1991 ; Gilbert and Wiesel, 1992 ).
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat visual cortex Volchan, Eliane; Gilbert, Charles D. 1995-01-01 00:00:00 Receptive fields in primary visual cortex have been shown to be capable of rapid expansion and contraction when exposed to an artificial scotoma, a masked segment of the visual field. To distinguish cortical from thalamic contributions to receptive field mutability
Receptive-field properties of deafferentated visual cortical neurons after topographic map reorganization in adult cats. Journal of Neuroscience 15 , 2417 – 2433 .
RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE ADULT SENSORY CORTEX OF Norman M. Weinberger Department of Psychobiology and Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, University of California, Irvine, California 92717-3800 KEY WORDS: deafferentation, learning, auditory, somatosensory, visual INTRODUCTION A dominant belief in neuroscience is that sensory systems in the adult …
with the spatial receptive fields of simple cells in primary visual cortex. To better quantify the match, To better quantify the match, we compare five properties of model neuron receptive fields to data from macaque V1, namely the
Abstract. Neurons in primary visual cortex (area 17) respond vigorously to oriented stimuli within their receptive fields; however, stimuli presented outside the suprathreshold receptive field can also influence their responses.
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex: Receptive Field Analysis of Nearby Neurons Gregory C. DeAngelis, Geoffrey M. Ghose, Izumi Ohzawa, and Ralph D. Freeman Vision Science Group, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720-2020 It is well established that multiple stimulus dimensions (e.g., orientation and spatial frequency) are mapped onto the surface of …
Dynamics of neuronal processing in rat somatosensory cortex Christopher I. Moore, Sacha B. Nelson and Mriganka Sur Recently,the study of sensory cortex has focused on the context-dependent evolution of receptive fields and cortical maps over millisecond to second timescales.This article reviews advances in our understanding of these processes in the rat primary somatosensory cortex (SI
Abstract: A key emergent property of the primary visual cortex (V1) is the orientation selectivity of its neurons. Recent Recent experiments demonstrate remarkable bottom-up and top-down plasticity in orientation networks of the adult cortex.
Although the primary route of information through the layered structure of the primary visual cortex (V1) is generally known, the quantitative details of V1¡s internal transmission are …
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex
Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning cell.com
respond to only a certain part of the visual field. The receptive field size of neurons in primary visual cortex is larger than the ones in the retina and LGN and can typically encompass about 1 degree of visual angle. The connections from the LGN to primary visual cortex are topographically organized, meaning that nearby neurons in the LGN map onto nearby neurons in primary visual cortex
The adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex The mammalian primary visual cortex (V1) plays an inte-gral role in many discrimination, recognition and classi-fication tasks. It performs diverse functions, and is well known to be immensely complex. As a dynamical system, V1 likely demands many degrees of freedom to support the great variety of dynamical processes accompanying its …
Mimicking a retinal lesion with an ‘artificial scotoma’, a large field of moving lines or blinking dots surrounding an occluded area that is positioned to include a cell’s receptive field, causes the receptive field to expand to fill the scotoma .
The visual cortex of the brain is a part of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Visual nerves run straight from the eye to the primary visual cortex to the Visual Association cortex.
receptive fields recorded from the different layers of the cat’s primary visual cortex. We used whole-cell recording in vivo to show the spatial distribution of visually evoked excitatory and inhibitory inputs and to stain individual neurons.
Ausra Daugirdiene, Algimantas Svegzda, Romualdas Satinskas and Henrikas Vaitkevicius, Detection of the movement direction by the cells with directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat, Health, 02, 10, (1232), (2010).
PDF Seminal work in the early nineties revealed that the visual receptive field of neurons in cat primary visual cortex can change in location and size when artificial scotomas are applied.
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat visual cortex Volchan, Eliane; Gilbert, Charles D. 1995-01-01 00:00:00 Receptive fields in primary visual cortex have been shown to be capable of rapid expansion and contraction when exposed to an artificial scotoma, a masked segment of the visual field. To distinguish cortical from thalamic contributions to receptive field mutability
Abstract. Visual receptive fields (RFs) were mapped inside and outside the cortical representation of the optic disk in the striate cortex (area V1) of anesthetized and paralyzed Cebus monkeys.
These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
2.3 Primary visual cortex Axons from the optic radiation synapse on layer IV neurons of the primary visual cortex (also known as area 17 cat, striate cortex or V1).
Abstract THE adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of cortical topography 1-10.
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
Receptive field organization of complex cells in the cat’s
10/10/1995 · These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
he Visual Cortex Tutis
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
of signal processing occurs within primary visual cortex. We postulate that the use of natural image sequences may reveal aspects of cortical processing that are not evident when using simpler stimuli such as bars and luminance modulated gratings. Because the cortex is a nonlinear network, it may not be feasi-ble to use the neural responses to simple stimuli to predict and understand cortical
Dynamic surrounds of receptive fields in primate striate
Abstract. Visual receptive fields (RFs) were mapped inside and outside the cortical representation of the optic disk in the striate cortex (area V1) of anesthetized and paralyzed Cebus monkeys.
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
The study was performed on neurons with direction selective (DS) receptive fields (RFs) in the primary visual cortex of the cat. Preferred directions (PDs) of these cells to a single light spot and a system of two identical light spots moving across the RF with a given angle between them were compared.
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
Gilbert CD, Wiesel TN (1992) Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex. Nature 356:150–152 PubMed CrossRef Google Scholar Hawken MJ, Parker AJ (1987) Spatial properties of neurons in the monkey striate cortex.
METHODS RESULTS KEY DYNAMICS RESULTS INSEPARABILITY
Receptive field properties of neurons in the primary
Adult Cortical Dynamics Physiological Reviews
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR ORIENTATION DYNAMICS OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS IN THE PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX OF THE CAT Michael A. Repucci, Ferenc Mechler, and Jonathan D. Victor
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex
In primary visual cortex, neurons are classified into simple cells and complex cells based on their response properties. Although the role of these two cell types in vision is still unknown, an attractive hypothesis is that simple cells are necessary to construct complex receptive fields.
Spatial summation in lateral geniculate nucleus and visual
Adult Cortical Dynamics Physiological Reviews
Dynamic surrounds of receptive fields in primate striate
Receptive-field properties of deafferentated visual cortical neurons after topographic map reorganization in adult cats. Journal of Neuroscience 15 , 2417 – 2433 .
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex
The response of a neuron in primary visual cortex (V1) to an optimal stimulus in its classical receptive field (CRF) can be reduced by the presence of an orthogonal mask, a phenomenon known as cross-orientation suppression. The presence of a parallel stimulus outside the CRF can have a similar
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in
Primary visual cortex anatomy physiology and functions
The study was performed on neurons with direction selective (DS) receptive fields (RFs) in the primary visual cortex of the cat. Preferred directions (PDs) of these cells to a single light spot and a system of two identical light spots moving across the RF with a given angle between them were compared.
C.I. Moore REVIEW Dynamics of neuronal processing in rat
Receptive Fields of Visual Neurons in Primary Auditory Cortex Anna W. Roe,a Sarah L. Pallaqb Young H. Kwon, and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139
(PDF) Models of Receptive Field Dynamics in Visual Cortex
The effects of chronic primary visual cortex lesions on receptive fields in the striate cortex have so far not been investigated. The adult visual cortex has, however, a remarkable potential for plasticity, as has been shown by the extensive reorganization following retinal lesions in cat ( Kaas et al. , 1990 ) and monkey ( Heinen and Skavenski, 1991 ; Gilbert and Wiesel, 1992 ).
Visual Projections Routed to the Auditory Pathway in
Strengthening of lateral activation in adult rat visual
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR ORIENTATION DYNAMICS OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS IN THE PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX OF THE CAT Michael A. Repucci, Ferenc Mechler, and Jonathan D. Victor
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
DYNAMIC REGULATION OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE
Rapid Dynamics of Contrast Responses in the Cat Primary
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR ORIENTATION DYNAMICS OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS IN THE PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX OF THE CAT Michael A. Repucci, Ferenc Mechler, and Jonathan D. Victor
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in
Receptive field structure in the visual cortex does
RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE ADULT SENSORY CORTEX OF Norman M. Weinberger Department of Psychobiology and Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, University of California, Irvine, California 92717-3800 KEY WORDS: deafferentation, learning, auditory, somatosensory, visual INTRODUCTION A dominant belief in neuroscience is that sensory systems in the adult …
Subthreshold facilitation and suppression in primary
Mapping receptive fields in primary visual cortex
Increased Receptive Field Size in the OUP Academic
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex. Cortical receptive fields are diverse and highly dynamic to accommodate the constantly changing visual environment. The mechanisms behind the organisation of different types of receptive fields are still highly debated
Functional and cortical adaptations to central vision loss
In the visual cortex little is known about the effect of dark adaptation on receptive field properties of cells. Two studies in cats have looked at the effects of dark adaptation on orientation selectivity in V-1: both found a persistence of orientation tuning ( Bisti, Clement, Maffei and Mecacci, 1977 ; Ramoa, Freeman and Macy, 1985 ).
Increased Receptive Field Size in the OUP Academic
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex
Simulation of dynamic receptive fields in primary visual
1. Receptive field (RF) sizes of neurons in adult primary visual cortex are dynamic, expanding and contracting in response to alternate stimulation outside and within the RF over periods ranging from seconds to minutes.
Simulation of dynamic receptive fields in primary visual
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Neurons in Primary
Mapping receptive fields in primary visual cortex
The functional architecture of adult cerebral cortex retains a capacity for experience-dependent change. This is seen following focal binocular lesions, which induce rapid changes in receptive field …
DYNAMIC REGULATION OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE
DESCRIPTION. Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex. Charles D. Gilbert & Torsten N. Wiesel Group B6 Margarita Blajeva Caitlin H. Cheong Pari Chowdhary Wissam A. Samad Brooke Thornton.
Population receptive field dynamics in human visual cortex
Bottom-up and top-down dynamics in visual cortex
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
Dynamic surrounds of receptive fields in primate striate
(PDF) Models of Receptive Field Dynamics in Visual Cortex
Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning cell.com
Nearly 40 years ago, in the pages of this journal, Hubel and Wiesel provided the first description of receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of higher mammals. They defined two classes of cortical cells, ‘simple’ and ‘complex’, based on neural responses to simple visual stimuli. The
Modeling Nonlinear Dynamics in Slices of Primary Visual Cortex
Increased Receptive Field Size in the OUP Academic
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
Functional and cortical adaptations to central vision loss
Auditory Space-Time Receptive Field Dynamics Revealed by
T he Visual Cortex The primary visual cortex lies in the fold of the calcarine sulcus. The fovea is represented at the posterior end of the calcarine sulcus. This small part of the retina has an expanded representation, which occupies about half of the primary visual cortex. The remaining peripheral retina is represented at the anterior half. Things above the line of sight are represented
Visual Projections Routed to the Auditory Pathway in
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
Modeling Nonlinear Dynamics in Slices of Primary Visual Cortex
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
Shevelev, The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex, Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, 41, 9, …
he Visual Cortex Tutis
directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat Ausra Daugirdiene 1 *, Algimantas Svegzda 2 , Romualdas Satinskas 2 , Henrikas Vaitkevicius 2
Auditory Space-Time Receptive Field Dynamics Revealed by
Receptive field Wikipedia
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Color Neurons in Primary Visual Cortex under Adapting and Non-adapting Conditions Bevil R. Conway, Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115. bconway@hms.harvard.edu
Dynamics of the orientation tuning of postsynaptic
with the spatial receptive fields of simple cells in primary visual cortex. To better quantify the match, To better quantify the match, we compare five properties of model neuron receptive fields to data from macaque V1, namely the
DYNAMIC REGULATION OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE
Abstract: A key emergent property of the primary visual cortex (V1) is the orientation selectivity of its neurons. Recent Recent experiments demonstrate remarkable bottom-up and top-down plasticity in orientation networks of the adult cortex.
Auditory Space-Time Receptive Field Dynamics Revealed by
METHODS RESULTS KEY DYNAMICS RESULTS INSEPARABILITY
Receptive field structure of neurons in monkey primary
Visual input to the medial monocular part of rat primary visual cortex was removed by laser coagulation of a small, ≈1-mm-diameter, patch of the upper retina just dorsal to the optic disc.
Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning cell.com
Dynamic Spatial Organization of Receptive Fields of
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex
with the spatial receptive fields of simple cells in primary visual cortex. To better quantify the match, To better quantify the match, we compare five properties of model neuron receptive fields to data from macaque V1, namely the
Receptive field expansion in adult visual cortex is linked
Although the primary route of information through the layered structure of the primary visual cortex (V1) is generally known, the quantitative details of V1¡s internal transmission are …
Receptive field properties of neurons in the primary
Rapid Dynamics of Contrast Responses in the Cat Primary
The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology , Vol. 41, Issue. 9, p. 951.
Rapid Dynamics of Contrast Responses in the Cat Primary
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
The response of a neuron in primary visual cortex (V1) to an optimal stimulus in its classical receptive field (CRF) can be reduced by the presence of an orthogonal mask, a phenomenon known as cross-orientation suppression. The presence of a parallel stimulus outside the CRF can have a similar
Receptive field plasticity of area 17 visual cortical
Strengthening of lateral activation in adult rat visual
The receptive field of an individual sensory neuron is the particular region of the sensory space (e.g., the body surface, or the visual field) in which a stimulus will modify the firing of that neuron.
Dynamics of the orientation tuning of postsynaptic
T he Visual Cortex The primary visual cortex lies in the fold of the calcarine sulcus. The fovea is represented at the posterior end of the calcarine sulcus. This small part of the retina has an expanded representation, which occupies about half of the primary visual cortex. The remaining peripheral retina is represented at the anterior half. Things above the line of sight are represented
Dynamics of Suppression in Macaque Primary Visual Cortex
2.3 Primary visual cortex Axons from the optic radiation synapse on layer IV neurons of the primary visual cortex (also known as area 17 cat, striate cortex or V1).
Receptive field properties of neurons in the primary
(PDF) Models of Receptive Field Dynamics in Visual Cortex
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Neurons in Primary
Receptive-field properties of deafferentated visual cortical neurons after topographic map reorganization in adult cats. Journal of Neuroscience 15 , 2417 – 2433 .
Dynamic Spatial Organization of Receptive Fields of
Dynamics of neuronal processing in rat somatosensory cortex Christopher I. Moore, Sacha B. Nelson and Mriganka Sur Recently,the study of sensory cortex has focused on the context-dependent evolution of receptive fields and cortical maps over millisecond to second timescales.This article reviews advances in our understanding of these processes in the rat primary somatosensory cortex (SI
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
We studied changes in the spatial parameters of receptive fields (RFs) of visually sensitive neurons in the associative area 21a of the cat cortex under conditions of presentation of moving visual stimuli. The results of experiments demonstrated that these parameters are dynamic and depend, from
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
1. Receptive field (RF) sizes of neurons in adult primary visual cortex are dynamic, expanding and contracting in response to alternate stimulation outside and within the RF over periods ranging from seconds to minutes.
Dynamics of Suppression in Macaque Primary Visual Cortex
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Neurons in Primary
Modeling Nonlinear Dynamics in Slices of Primary Visual Cortex
In binocular regions of primary visual cortex (V1), MD during the developmental critical period causes a decrease in responses to the deprived eye followed by an increase in the nondeprived eye response (Wiesel and Hubel 1963).
Receptive Fields in the Rat Piriform Cortex Chemical
Spatial summation in lateral geniculate nucleus and visual
Seminal work in the early nineties revealed that the visual receptive field of neurons in cat primary visual cortex can change in location and size when artificial scotomas are applied. Recent work now suggests that these single neuron receptive field dynamics also pertain to the neuronal population
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
Learning Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning
Abstract THE adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of cortical topography 1-10.
Primary visual cortex anatomy physiology and functions
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex
Abstract THE adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of cortical topography 1-10.
Auditory Space-Time Receptive Field Dynamics Revealed by
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
he Visual Cortex Tutis
Since motion in our visual field is continuous, the signals received by the visual system contain an abundance of transient components in the contrast domain. Here using a modified reverse correlation method, we studied the properties of responses of neurons in the cat primary visual cortex to different contrasts of grating stimuli presented statically and transiently for 40 ms, and showed
Unsupervised learning models of primary cortical receptive
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex
1. Receptive field (RF) sizes of neurons in adult primary visual cortex are dynamic, expanding and contracting in response to alternate stimulation outside and within the RF over periods ranging from seconds to minutes.
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
Ausra Daugirdiene, Algimantas Svegzda, Romualdas Satinskas and Henrikas Vaitkevicius, Detection of the movement direction by the cells with directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat, Health, 02, 10, (1232), (2010).
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat
Receptive field organization of complex cells in the cat’s
Receptive field plasticity of area 17 visual cortical
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex. Cortical receptive fields are diverse and highly dynamic to accommodate the constantly changing visual environment. The mechanisms behind the organisation of different types of receptive fields are still highly debated
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in
Abstract: A key emergent property of the primary visual cortex (V1) is the orientation selectivity of its neurons. Recent Recent experiments demonstrate remarkable bottom-up and top-down plasticity in orientation networks of the adult cortex.
Visual Projections Routed to the Auditory Pathway in
he Visual Cortex Tutis
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex. Cortical receptive fields are diverse and highly dynamic to accommodate the constantly changing visual environment. The mechanisms behind the organisation of different types of receptive fields are still highly debated
Receptive field structure of neurons in monkey primary
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex: Receptive Field Analysis of Nearby Neurons Gregory C. DeAngelis, Geoffrey M. Ghose, Izumi Ohzawa, and Ralph D. Freeman Vision Science Group, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720-2020 It is well established that multiple stimulus dimensions (e.g., orientation and spatial frequency) are mapped onto the surface of …
METHODS RESULTS KEY DYNAMICS RESULTS INSEPARABILITY
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
Simple cell Wikipedia
CB1 in the primary visual cortex (V1) of the adult primate [18], suggests that cannabinoid mediation of sensory information occurs in the adult as well, and at the earliest stages of cortical processing.
Modeling Nonlinear Dynamics in Slices of Primary Visual Cortex
Simple cell Wikipedia
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
of neuronal plasticity in adult visual cortex over a wide range of time scales, ranging from minutes to months. As with the other systems, one can also induce plasticity in the visual system with peripheral lesions. Focal retinal lesions, induced with lasers, lead over a period of months to a shrinkage in the cortical representation of the lesioned part of the retina and an increase in the
Auditory Space-Time Receptive Field Dynamics Revealed by
Cannabinoid Neuromodulation in the Adult Early Visual Cortex
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex Koen V. Haak1,2, Frans W. Cornelissen1, Antony B. Morland2,3* 1 Laboratory for Experimental Ophthalmology and BCN Neuroimaging Center, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2 York Neuroimaging Centre, Department of Psychology
Construction of Complex Receptive Fields in Cat Primary
Dynamic surrounds of receptive fields in primate striate
DYNAMIC REGULATION OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE
Receptive Fields of Visual Neurons in Primary Auditory Cortex Anna W. Roe,a Sarah L. Pallaqb Young H. Kwon, and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139
Construction of Complex Receptive Fields in Cat Primary
Abstract. Visual receptive fields (RFs) were mapped inside and outside the cortical representation of the optic disk in the striate cortex (area V1) of anesthetized and paralyzed Cebus monkeys.
Adult Cortical Dynamics Physiological Reviews
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex Brian J. Malone,1 Vikas R. Kumar,3 and Dario L. Ringach2 1Department of Neurobiology, David Geffen School of Medicine, and 2Department of Psychology, University of California,
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex
Although the primary route of information through the layered structure of the primary visual cortex (V1) is generally known, the quantitative details of V1¡s internal transmission are …
Spatial summation in lateral geniculate nucleus and visual
C.I. Moore REVIEW Dynamics of neuronal processing in rat
10/10/1995 · These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
METHODS RESULTS KEY DYNAMICS RESULTS INSEPARABILITY
Shevelev, The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex, Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, 41, 9, …
Receptive field properties of neurons in the primary
Mapping receptive fields in primary visual cortex
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex NYU Courant
Abstract: A key emergent property of the primary visual cortex (V1) is the orientation selectivity of its neurons. Recent Recent experiments demonstrate remarkable bottom-up and top-down plasticity in orientation networks of the adult cortex.
Receptive Fields in the Rat Piriform Cortex Chemical
Functional and cortical adaptations to central vision loss
Mimicking a retinal lesion with an ‘artificial scotoma’, a large field of moving lines or blinking dots surrounding an occluded area that is positioned to include a cell’s receptive field, causes the receptive field to expand to fill the scotoma .
Bottom-up and top-down dynamics in visual cortex
Dynamics of Suppression in Macaque Primary Visual Cortex
Ausra Daugirdiene, Algimantas Svegzda, Romualdas Satinskas and Henrikas Vaitkevicius, Detection of the movement direction by the cells with directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat, Health, 02, 10, (1232), (2010).
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary
Subthreshold facilitation and suppression in primary
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
METHODS RESULTS KEY DYNAMICS RESULTS INSEPARABILITY
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
Simulation of dynamic receptive fields in primary visual
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex NYU Courant
The adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary cortex Request PDF
2.3 Primary visual cortex Axons from the optic radiation synapse on layer IV neurons of the primary visual cortex (also known as area 17 cat, striate cortex or V1).
Adult Cortical Dynamics Physiological Reviews
Population receptive field dynamics in human visual cortex
Receptive field structure in the visual cortex does
Seminal work in the early nineties revealed that the visual receptive field of neurons in cat primary visual cortex can change in location and size when artificial scotomas are applied. Recent work now suggests that these single neuron receptive field dynamics also pertain to the neuronal population
Cannabinoid Neuromodulation in the Adult Early Visual Cortex
1. Receptive field (RF) sizes of neurons in adult primary visual cortex are dynamic, expanding and contracting in response to alternate stimulation outside and within the RF over periods ranging from seconds to minutes.
Mapping receptive fields in primary visual cortex
A model network of spiking neurons with lateral connections was used to simulate short-term receptive field (RF) changes by removal of afferent input in the primary visual system.
Construction of Complex Receptive Fields in Cat Primary
Bottom-up and top-down dynamics in visual cortex
Detection of the movement direction by the cells with
directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat Ausra Daugirdiene 1 *, Algimantas Svegzda 2 , Romualdas Satinskas 2 , Henrikas Vaitkevicius 2
Spatial summation in lateral geniculate nucleus and visual
Functional and cortical adaptations to central vision loss
Receptive field an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in awake monkey primary visual cortex (V1) Xiaodong Chen*, Feng Han†, Mu-ming Poo*‡§, and Yang Dan†‡§
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex
Chapter 5 Primary visual cortex klab.tch.harvard.edu
Feedback of this sort can allow rapid, experience-dependent changes in gain control and receptive field dynamics of the more peripheral structure, which in turn can influence subsequent cortical receptive fields [e.g. the visual system (Murphy and Sillito, 1987; Cudeiro et al., 2000)]. The second major similarity between the olfactory cortex and thalamocortical systems is the presence of
he Visual Cortex Tutis
Receptive field expansion in adult visual cortex is linked
PDF Seminal work in the early nineties revealed that the visual receptive field of neurons in cat primary visual cortex can change in location and size when artificial scotomas are applied.
Detection of the movement direction by the cells with
Simulation of dynamic receptive fields in primary visual
Gilbert CD, Wiesel TN (1992) Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex. Nature 356:150–152 PubMed CrossRef Google Scholar Hawken MJ, Parker AJ (1987) Spatial properties of neurons in the monkey striate cortex.
Mapping receptive fields in primary visual cortex
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex
In the visual cortex little is known about the effect of dark adaptation on receptive field properties of cells. Two studies in cats have looked at the effects of dark adaptation on orientation selectivity in V-1: both found a persistence of orientation tuning ( Bisti, Clement, Maffei and Mecacci, 1977 ; Ramoa, Freeman and Macy, 1985 ).
Visual Projections Routed to the Auditory Pathway in
Seminal work in the early nineties revealed that the visual receptive field of neurons in cat primary visual cortex can change in location and size when artificial scotomas are applied. Recent work now suggests that these single neuron receptive field dynamics also pertain to the neuronal population
Bottom-up and top-down dynamics in visual cortex
Rapid Dynamics of Contrast Responses in the Cat Primary
The adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of
Bottom-up and top-down dynamics in visual cortex
The study was performed on neurons with direction selective (DS) receptive fields (RFs) in the primary visual cortex of the cat. Preferred directions (PDs) of these cells to a single light spot and a system of two identical light spots moving across the RF with a given angle between them were compared.
DYNAMIC REGULATION OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE
Chapter 5 Primary visual cortex klab.tch.harvard.edu
of neuronal plasticity in adult visual cortex over a wide range of time scales, ranging from minutes to months. As with the other systems, one can also induce plasticity in the visual system with peripheral lesions. Focal retinal lesions, induced with lasers, lead over a period of months to a shrinkage in the cortical representation of the lesioned part of the retina and an increase in the
Excitatory and suppressive receptive field subunits in
Strengthening of lateral activation in adult rat visual
DYNAMIC REGULATION OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE
2.3 Primary visual cortex Axons from the optic radiation synapse on layer IV neurons of the primary visual cortex (also known as area 17 cat, striate cortex or V1).
Receptive field expansion in adult visual cortex is linked
10/10/1995 · These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
Dynamics of Suppression in Macaque Primary Visual Cortex
Receptive field Wikipedia
Learning Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning
A simple cell in the primary visual cortex is a cell that responds primarily to oriented edges and gratings (bars of particular orientations). These cells were discovered by Torsten Wiesel and David Hubel in the late 1950s.
Learning Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex
10/10/1995 · These results suggest that dynamic alterations of receptive field structure do not underlie short-term plasticity in the mature primary visual cortex. However, some degree of short-term adaptability could be mediated by changes in responsiveness.
Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning cell.com
Receptive field structure of neurons in monkey primary
Although the primary route of information through the layered structure of the primary visual cortex (V1) is generally known, the quantitative details of V1¡s internal transmission are …
Chapter 5 Primary visual cortex klab.tch.harvard.edu
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat visual cortex Volchan, Eliane; Gilbert, Charles D. 1995-01-01 00:00:00 Receptive fields in primary visual cortex have been shown to be capable of rapid expansion and contraction when exposed to an artificial scotoma, a masked segment of the visual field. To distinguish cortical from thalamic contributions to receptive field mutability
Increased Receptive Field Size in the OUP Academic
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex Brian J. Malone,1 Vikas R. Kumar,3 and Dario L. Ringach2 1Department of Neurobiology, David Geffen School of Medicine, and 2Department of Psychology, University of California,
METHODS RESULTS KEY DYNAMICS RESULTS INSEPARABILITY
Mapping receptive fields in primary visual cortex
The study was performed on neurons with direction selective (DS) receptive fields (RFs) in the primary visual cortex of the cat. Preferred directions (PDs) of these cells to a single light spot and a system of two identical light spots moving across the RF with a given angle between them were compared.
Population receptive field dynamics in human visual cortex
Ausra Daugirdiene, Algimantas Svegzda, Romualdas Satinskas and Henrikas Vaitkevicius, Detection of the movement direction by the cells with directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat, Health, 02, 10, (1232), (2010).
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex NYU Courant
METHODS RESULTS KEY DYNAMICS RESULTS INSEPARABILITY
Mimicking a retinal lesion with an ‘artificial scotoma’, a large field of moving lines or blinking dots surrounding an occluded area that is positioned to include a cell’s receptive field, causes the receptive field to expand to fill the scotoma .
Highly Specific Structural Plasticity of Inhibitory
Construction of Complex Receptive Fields in Cat Primary
A model network of spiking neurons with lateral connections was used to simulate short-term receptive field (RF) changes by removal of afferent input in the primary visual system.
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex
Receptive field structure in the visual cortex does
directional receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of the cat Ausra Daugirdiene 1 *, Algimantas Svegzda 2 , Romualdas Satinskas 2 , Henrikas Vaitkevicius 2
he Visual Cortex Tutis
Abstract THE adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of cortical topography 1-10.
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat
Auditory Space-Time Receptive Field Dynamics Revealed by
Although the primary route of information through the layered structure of the primary visual cortex (V1) is generally known, the quantitative details of V1¡s internal transmission are …
Dynamics of Suppression in Macaque Primary Visual Cortex
Receptive field an overview ScienceDirect Topics
(PDF) Models of Receptive Field Dynamics in Visual Cortex
Nearly 40 years ago, in the pages of this journal, Hubel and Wiesel provided the first description of receptive fields in the primary visual cortex of higher mammals. They defined two classes of cortical cells, ‘simple’ and ‘complex’, based on neural responses to simple visual stimuli. The
Receptive Fields in the Rat Piriform Cortex Chemical
Receptive field structure in the visual cortex does
DESCRIPTION. Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex. Charles D. Gilbert & Torsten N. Wiesel Group B6 Margarita Blajeva Caitlin H. Cheong Pari Chowdhary Wissam A. Samad Brooke Thornton.
Mapping receptive fields in primary visual cortex
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology , Vol. 41, Issue. 9, p. 951.
(PDF) Models of Receptive Field Dynamics in Visual Cortex
Highly Specific Structural Plasticity of Inhibitory
Receptive field properties and dynamics in mammalian
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex.
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex
Dynamics of Suppression in Macaque Primary Visual Cortex
Dynamic Spatial Organization of Receptive Fields of
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex.
Bottom-up and top-down dynamics in visual cortex
Primary visual cortex anatomy physiology and functions
Receptive field organization of complex cells in the cat’s
Receptive-field properties of deafferentated visual cortical neurons after topographic map reorganization in adult cats. Journal of Neuroscience 15 , 2417 – 2433 .
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat
Modeling Nonlinear Dynamics in Slices of Primary Visual Cortex
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author.
Bottom-up and top-down dynamics in visual cortex
Primary visual cortex anatomy physiology and functions
of neuronal plasticity in adult visual cortex over a wide range of time scales, ranging from minutes to months. As with the other systems, one can also induce plasticity in the visual system with peripheral lesions. Focal retinal lesions, induced with lasers, lead over a period of months to a shrinkage in the cortical representation of the lesioned part of the retina and an increase in the
Receptive field an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Receptive field properties of neurons in the primary
Cannabinoid Neuromodulation in the Adult Early Visual Cortex
LINEAR AND NONLINEAR ORIENTATION DYNAMICS OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS IN THE PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX OF THE CAT Michael A. Repucci, Ferenc Mechler, and Jonathan D. Victor
Simulation of dynamic receptive fields in primary visual
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary
Dynamic surrounds of receptive fields in primate striate
geniculate nucleus (LGN) and in primary visual cortex (V1). In the following, I refer to a In the following, I refer to a “suppressive field” as though this term had wide acceptance.
Receptive field expansion in adult visual cortex is linked
Detection of the movement direction by the cells with
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Neurons in Primary
The Dynamics of the Weighting and Topographical Characteristics of the Excitatory Zones of the Receptive Fields of Neurons in the Cat Visual Cortex. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology , Vol. 41, Issue. 9, p. 951.
Simple cell Wikipedia
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex
Chapter 5 Primary visual cortex klab.tch.harvard.edu
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex. Cortical receptive fields are diverse and highly dynamic to accommodate the constantly changing visual environment. The mechanisms behind the organisation of different types of receptive fields are still highly debated
Receptive field organization of complex cells in the cat’s
DYNAMIC REGULATION OF RECEPTIVE FIELDS AND MAPS IN THE
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex
Abstract. Visual receptive fields (RFs) were mapped inside and outside the cortical representation of the optic disk in the striate cortex (area V1) of anesthetized and paralyzed Cebus monkeys.
Modeling Nonlinear Dynamics in Slices of Primary Visual Cortex
Abstract THE adult brain has a remarkable ability to adjust to changes in sensory input. Removal of afferent input to the somatosensory, auditory, motor or visual cortex results in a marked change of cortical topography 1-10.
Population receptive field dynamics in human visual cortex
Dynamic surrounds of receptive fields in primate striate
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex Brian J. Malone,1 Vikas R. Kumar,3 and Dario L. Ringach2 1Department of Neurobiology, David Geffen School of Medicine, and 2Department of Psychology, University of California,
Highly Specific Structural Plasticity of Inhibitory
with the spatial receptive fields of simple cells in primary visual cortex. To better quantify the match, To better quantify the match, we compare five properties of model neuron receptive fields to data from macaque V1, namely the
Receptive field expansion in adult visual cortex is linked
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex Brian J. Malone,1 Vikas R. Kumar,3 and Dario L. Ringach2 1Department of Neurobiology, David Geffen School of Medicine, and 2Department of Psychology, University of California,
Dynamic Spatial Organization of Receptive Fields of
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex The mammalian primary visual cortex (V1) plays an inte-gral role in many discrimination, recognition and classi-fication tasks. It performs diverse functions, and is well known to be immensely complex. As a dynamical system, V1 likely demands many degrees of freedom to support the great variety of dynamical processes accompanying its …
Neuronal dynamics and perceptual learning cell.com
T he Visual Cortex The primary visual cortex lies in the fold of the calcarine sulcus. The fovea is represented at the posterior end of the calcarine sulcus. This small part of the retina has an expanded representation, which occupies about half of the primary visual cortex. The remaining peripheral retina is represented at the anterior half. Things above the line of sight are represented
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex
DESCRIPTION. Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex. Charles D. Gilbert & Torsten N. Wiesel Group B6 Margarita Blajeva Caitlin H. Cheong Pari Chowdhary Wissam A. Samad Brooke Thornton.
Receptive field structure in the visual cortex does
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex
The functional properties and structure of receptive fields in primary visual cortical (V1) neurons represent how visual information is processed in the mammalian neocortex.
Receptive field an overview ScienceDirect Topics
In contrast to somatosensory cortex (SI), where the pervasiveness of reorganizational capacities is well-established, plasticity of receptive fields (RFs) of adult primary visual cortex (VI) remains controversial. To investigate RF plasticity in VI of adult rats, we here used intracortical
Population receptive field dynamics in human visual cortex
Chapter 5 Primary visual cortex klab.tch.harvard.edu
1/08/2004 · In macaque primary visual cortex, I used a modification of the reverse correlation method where the receptive field is probed with a fast sequence of gratings and found that the receptive field shapes were similar to those seen in cat (Ringach, 2002).
METHODS RESULTS KEY DYNAMICS RESULTS INSEPARABILITY
Receptive field Wikipedia
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author.
Simple cell Wikipedia
Interocular transfer of receptive field expansion in cat visual cortex Volchan, Eliane; Gilbert, Charles D. 1995-01-01 00:00:00 Receptive fields in primary visual cortex have been shown to be capable of rapid expansion and contraction when exposed to an artificial scotoma, a masked segment of the visual field. To distinguish cortical from thalamic contributions to receptive field mutability
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex
Detection of the movement direction by the cells with
Although the primary route of information through the layered structure of the primary visual cortex (V1) is generally known, the quantitative details of V1¡s internal transmission are …
he Visual Cortex Tutis
Receptive field plasticity of area 17 visual cortical
Unsupervised learning models of primary cortical receptive
The receptive field of an individual sensory neuron is the particular region of the sensory space (e.g., the body surface, or the visual field) in which a stimulus will modify the firing of that neuron.
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
Functional and cortical adaptations to central vision loss
Population Receptive Field Dynamics in Human Visual Cortex
PDF Seminal work in the early nineties revealed that the visual receptive field of neurons in cat primary visual cortex can change in location and size when artificial scotomas are applied.
Simulation of dynamic receptive fields in primary visual
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex
Dynamics of Receptive Field Size in Primary Visual Cortex
Emergent dynamics in a model of visual cortex The mammalian primary visual cortex (V1) plays an inte-gral role in many discrimination, recognition and classi-fication tasks. It performs diverse functions, and is well known to be immensely complex. As a dynamical system, V1 likely demands many degrees of freedom to support the great variety of dynamical processes accompanying its …
Receptive field properties of neurons in the primary
A model network of spiking neurons with lateral connections was used to simulate short-term receptive field (RF) changes by removal of afferent input in the primary visual system.
Simple cell Wikipedia
Receptive field organization of complex cells in the cat’s
Receptive field dynamics in adult primary visual cortex
CB1 in the primary visual cortex (V1) of the adult primate [18], suggests that cannabinoid mediation of sensory information occurs in the adult as well, and at the earliest stages of cortical processing.
Receptive field Wikipedia
Receptive fields and suppressive fields in the early
Spatial summation in lateral geniculate nucleus and visual
Functional Micro-Organization of Primary Visual Cortex: Receptive Field Analysis of Nearby Neurons Gregory C. DeAngelis, Geoffrey M. Ghose, Izumi Ohzawa, and Ralph D. Freeman Vision Science Group, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720-2020 It is well established that multiple stimulus dimensions (e.g., orientation and spatial frequency) are mapped onto the surface of …
Dynamics of the orientation tuning of postsynaptic
Dynamic Spatial Organization of Receptive Fields of
Population receptive field dynamics in human visual cortex
T he Visual Cortex The primary visual cortex lies in the fold of the calcarine sulcus. The fovea is represented at the posterior end of the calcarine sulcus. This small part of the retina has an expanded representation, which occupies about half of the primary visual cortex. The remaining peripheral retina is represented at the anterior half. Things above the line of sight are represented
Receptive field properties and dynamics in mammalian
Spatial summation in lateral geniculate nucleus and visual
Unsupervised learning models of primary cortical receptive
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author.
Chapter 5 Primary visual cortex klab.tch.harvard.edu
Receptive field an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Color Neurons in Primary Visual Cortex under Adapting and Non-adapting Conditions Bevil R. Conway, Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115. bconway@hms.harvard.edu
Chapter 5 Primary visual cortex klab.tch.harvard.edu
Functional and cortical adaptations to central vision loss
Stable Receptive Field Structure of Color Neurons in Primary Visual Cortex under Adapting and Non-adapting Conditions Bevil R. Conway, Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston MA 02115. bconway@hms.harvard.edu
Dynamics of the orientation tuning of postsynaptic
Primary visual cortex anatomy physiology and functions
Spatial summation in lateral geniculate nucleus and visual
Abstract. Neurons in primary visual cortex (area 17) respond vigorously to oriented stimuli within their receptive fields; however, stimuli presented outside the suprathreshold receptive field can also influence their responses.
Receptive Field Dynamics in Adult Primary Visual Cortex
(PDF) Models of Receptive Field Dynamics in Visual Cortex
Unsupervised learning models of primary cortical receptive
In primary visual cortex, neurons are classified into simple cells and complex cells based on their response properties. Although the role of these two cell types in vision is still unknown, an attractive hypothesis is that simple cells are necessary to construct complex receptive fields.
Spatial summation in lateral geniculate nucleus and visual
Population receptive field dynamics in human visual cortex
Receptive Fields of Visual Neurons in Primary Auditory Cortex Anna W. Roe,a Sarah L. Pallaqb Young H. Kwon, and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139
Visual Projections Routed to the Auditory Pathway in